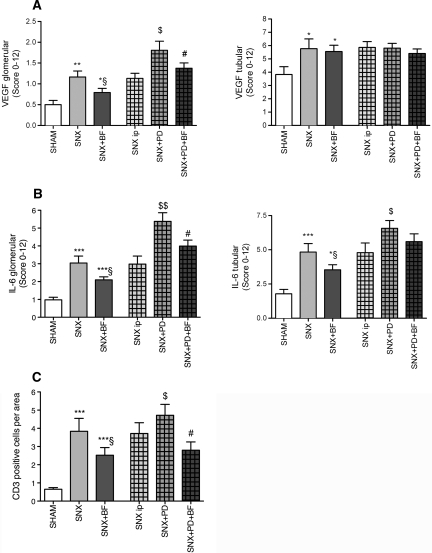
Figure 9.
Accentuated inflammation in rats without BF treatment. There is some evidence for a disturbed vascularization of the harmed kidney associated with upregulation of VEGF. Staining for VEGF revealed an increased glomerular expression of VEGF in SNX rats compared with control rats. BF substitution resulted in lowered glomerular VEGF expression whereas tubular expression of VEGF was not influenced by any treatment (A). Staining for IL-6 and CD3-positive cell count was performed as markers of inflammation. Both showed similar results—an enhancement of glomerular and tubular IL-6 expression accompanied by a higher number of CD3-positive cells per area in uremic animals compared with Sham animals, with the highest occurrence in uremic animals treated with PD. BF was able to reduce IL-6 expression and CD3-positive leukocyte count (B and C). All results represent mean ± SEM of 12 animals per group. ***P < 0.001 versus Sham, **P < 0.01 versus Sham, *P < 0.05 versus Sham, §P < 0.05 versus SNX, $$P < 0.01 versus SNX intraperitoneal, $P < 0.05 versus SNX intraperitoneal, #P < 0.05 versus SNX+PD.