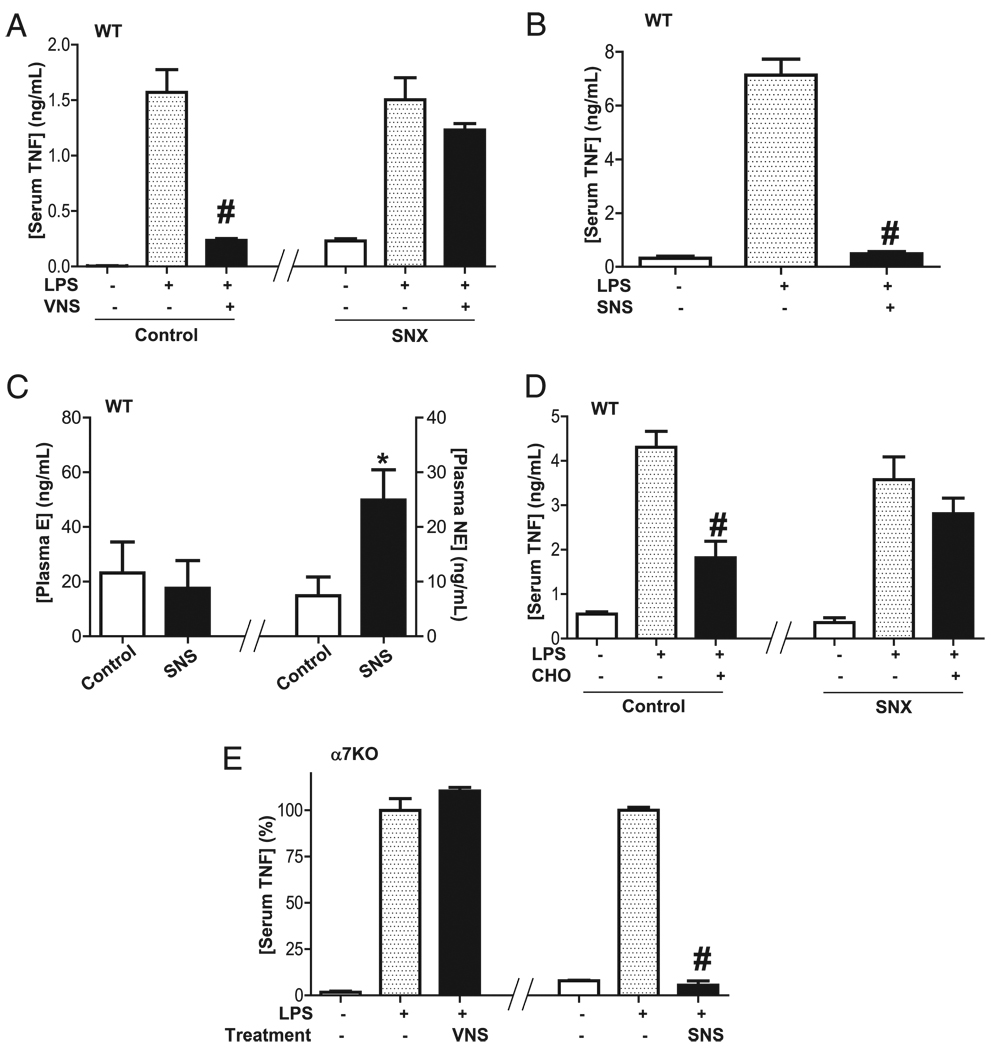
FIGURE 4.
Vagus nerve and α7nAChR agonists control systemic inflammation through the splenic nerve. A, C57BL/6J WT mice underwent vagotomy (VGX) and sham (control) or splenic neurectomy (SNX) 24 h before endotoxemia (LPS) and cervical vagal stimulation (VNS). Serum TNF levels were analyzed at 90 min after endotoxemia. B and C, C57BL/6J WT mice underwent SNS, and (B) serum TNF (C) or plasma epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) were analyzed by ELISA. D, C57BL/6J WT mice underwent sham or splenic neurectomy (SNX) 24 h before treatments. Selective α7nAChR agonist choline (CHO; 15 mg/kg i.p.) was administered 30 min before LPS (6 mg/kg i.p.). E, SNS re-establishes neuromodulation in α7nAChR knockout mice. Knockout mice underwent vagotomy 24 h before endotoxemia (LPS). Animals received VNS or SNS. #p < 0.01 versus LPS (n = 3; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s corrections), *p < 0.01 versus control (n = 4; Mann–Whitney U test