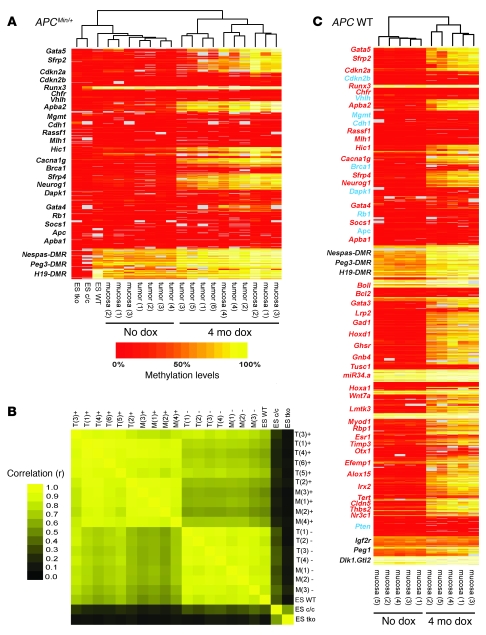
Figure 1. DNA methylation analysis of colon tumors and colon epithelial cells with or without Dnmt3b transgene expression.
4 mo dox, Dnmt3b induction; no dox, no Dnmt3b induction; ES c/c, Dnmt1-deficient ES cells; ES tko, Dnmt1/Dnmt3a/Dnmt3b triple-knockout ES cells; gray, no data. Heat map data were generated by mass array analysis and subjected to sample-based unsupervised hierarchical clustering. (A) Tumors and mucosa samples with Dnmt3b induction showed reproducible de novo DNA methylation of specific genomic loci. Imprinted regions (Nespas-, Peg3-, and H19-DMR) were partially methylated; ES tko and ES c/c cells showed loss of DNA methylation. (B) Pairwise correlation of methylation data confirmed similar de novo methylation in all samples with Dnmt3b induction (r, 0.76–0.97; mean r, 0.90). (C) Dnmt3b-mediated DNA methylation in colon mucosa of APC WT mice closely resembled de novo methylation reported for human colon cancer (Supplemental Table 1), which suggests that Dnmt3b can induce cancer-specific de novo methylation in normal cells (red, methylated; blue, unmethylated; black, control/imprinted regions).