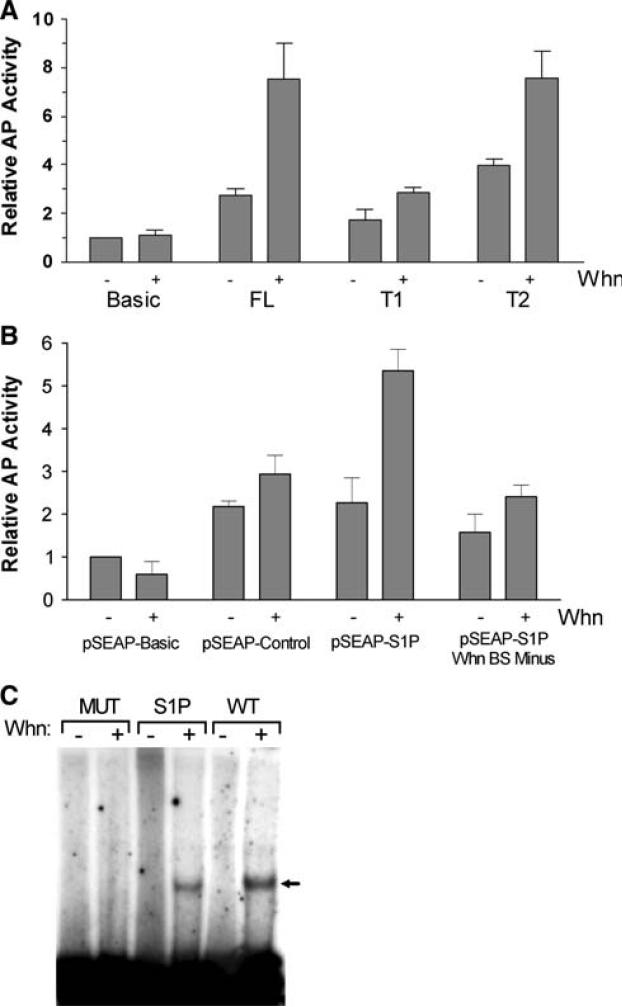
Fig. 4.
Whn effects on the cloned SUMO1 promoter. a The full-length pSEAP-SUMO1 promoter (FL) and two truncations (T1 and T2) were co-transfected into HaCaT cells with either 3 μg of pCDNA (−lanes) or 3 μg of the Whn expression vector (+lanes). Supernatants were collected at 48 h post-transfections and analyzed for AP activity. Activity results were normalized to the value for the negative control (pSEAP-BASIC) in the absence of Whn. The increase in the FL and T2 samples in the presence of Whn was statistically significant (P < 0.05), while the increase for T1 was not. b The various plasmids indicated were transfected in HaCaT cells with pCDNA (−lanes) or with the Whn plasmid (+lanes) as in part a. The pSEAP-S1P Whn BS Minus plasmid was constructed from the pSEAP-S1Promoter and contains a CG to TA change in the core motif of the Whn binding site. Samples were collected and analyzed as in part a and represent the average of 2–3 independent experiments. Only the increase seen with pSEAP-S1P in the presence of Whn was statistically significant (P < 0.05). c EMSA analysis of the purified Whn DNA binding domain (WhnDBD) protein. WhnDBD binding to three different oligonucleotides was determined by EMSA as described in “Material and methods”. The WT oligonucleotide was as described previously [20] and contains a strong Whn binding site. The SUMO1P (S1P) oligonucleotide is derived from the SUMO1 promoter region and contains the predicted Whn binding site. The MUT oligonucleotide has the CG from the critical ACGC core motif of the Whn binding site changed to TA, a change which was previously shown to eliminate WhnDBD binding [20]. Minus (−) lanes contained a comparable amount of the bovine papillomavirus E2 DNA binding protein as a specificity control. No E2 binding site was present in the oligo substrates