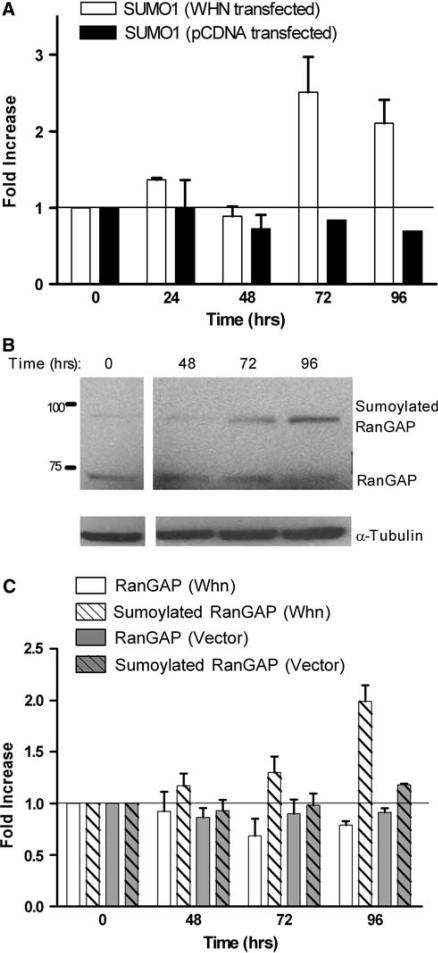
Fig. 5.
Effect of Whn on the endogenous SUMO1 promoter and overall sumoylation. a HaCaT cells were transfected with the Whn expression vector (WHN transfected) or the empty parental vector (pCDNA transfected) as indicated. RNA was collected at 24 h intervals from 0 to 96 h post-transfection, and the SUMO1 transcript was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. SUMO1 transcript values were normalized to the 18S RNA value for each sample and then compared to the 0 time samples. The increase in the SUMO1 transcripts in the presence of Whn at 72 and 96 h was statistically significant (P < 0.05). b HaCaT cells were transfected with the Whn expression vector, and total protein extracts were prepared at times 0, 48, 72, and 96 h post-transfection. Samples were electrophoresed on a 10% SDS polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with anti-RanGAP1 and anti-tubulin. The positions of the molecular weight markers in kDa are indicated on the left. c The relative levels of RanGAP1 and sumoylated RanGAP1 were quantitated by densitometric analysis of immunoblots such as shown in b. HaCaT cells were transfected with either the Whn expression vector (Whn samples) or the empty parental pCDNA plasmid (Vector samples), and extracts were prepared and immunoblotted as in b. The quantitation represents the average of three experiments. Compared to the 0 time sample, the increase in sumoylated RanGAP seen in the presence of Whn at 96 h was statistically significant (P < 0.05). None of the other samples showed any significant change