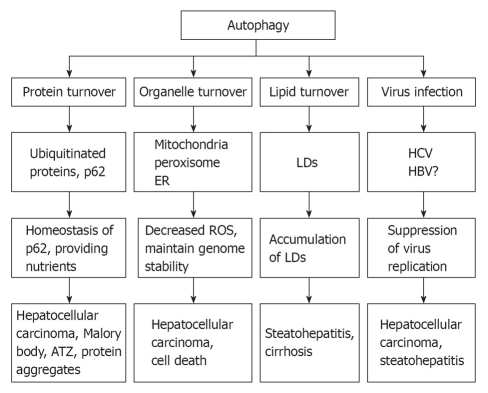
Figure 3.
Role of autophagy in liver pathophysiology. At least 4 different roles that autophagy may play in liver physiology and liver diseases: remove misfolded proteins, regulate hepatocellular organelle turn over, maintain hepatic lipid homeostasis, and influence hepatitis virus infection. As a result, defects in autophagy may lead to accumulation of alcoholic Mallory bodies, α-antitrypsin deficiency-induced liver injury, increased hepatocyte cell death, steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; LDs: Lipid droplets.