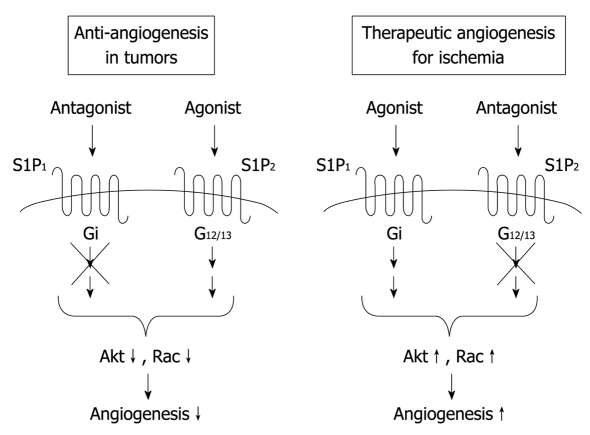
Figure 3.
Possible therapeutic strategies for anti-angiogenesis in tumors and angiogenesis in ischemic diseases. S1P1 and S1P2 mediate angiogenic and anti-angiogenic effects of S1P in vivo, respectively. Therefore, it is possible that simultaneous activation of the angiogenic receptor S1P1 and blockade of the anti-angiogenic receptor S1P2 are more effective for therapeutic angiogenesis in ischemic diseases compared with S1P1 activation or S1P2 inhibition alone. In contrast, for anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer, the combination of S1P1 inhibition and S1P2 stimulation might be favorable.