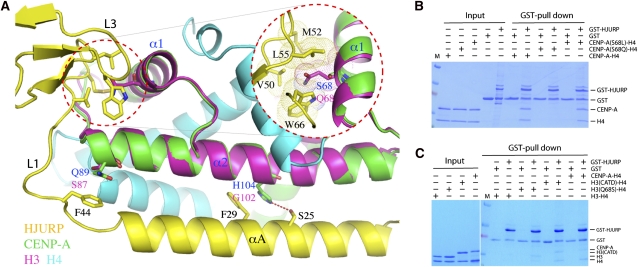
Figure 5.
Determinants of CENP-A specificity. (A) His 104 and Gln 89, shown in the CATD of CENP-A (α2 and loop-1), make CENP-A-specific contacts with HJURP. Histone H3 (magenta) of a H3–H4 heterodimer (PBD ID: 1KX5) is superimposed with CENP-A. CENP-A residues making specific contacts, H3 residues in corresponding positions, and HJURP residues involved in the interactions are shown in a stick model. Selected residues of CENP-A, H3, and HJURP are labeled with blue, magenta, and black letters, respectively. An inset encircled with a red dashed line shows the interaction site of Ser 68 of CENP-A located outside of the CATD and surrounding HJURP residues. The atomic radii of side chain atoms of the Ser 68 counterpart in H3, Gln 68, and HJURP residues are shown in a dot model to indicate unfavorable packing of Gln 68. (B) GST pull-down experiments showing the effect of HJURP binding to CENP-A with Ser 68 mutations. (C) GST pull-downs with the H3–H4, H3(Q68S)–H4, H3CATD–H4, and CENP-A–H4 complexes. To lower the background level of H3–H4 binding, 0.05% NP-40 in the washing buffer was used, compared with 0.025% NP-40 in B.