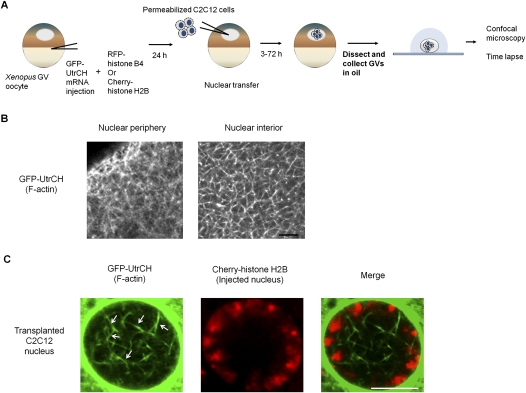
Figure 1.
Visualization of nuclear F-actin. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental strategy to visualize nuclear F-actin formed in transplanted nuclei. Injected nuclei cannot be observed without dissecting GVs. Dissected GVs can be maintained alive in mineral oil and are transparent enough to observe their interior structure by confocal microscopy. (B) Nuclear F-actin in a Xenopus oocyte nucleus, visualized with GFP-UtrCH probes. A meshwork structure of nuclear F-actin is naturally formed in nucleoplasm. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Nuclear F-actin is observed in injected nuclei. F-actin was labeled with GFP-UtrCH (green) and chromatin of injected nuclei was visualized with Cherry-histone H2B (red). Actin bundles in a transplanted nucleus are marked with white arrows. The image was taken 24 h after NT. Bar, 10 μm.