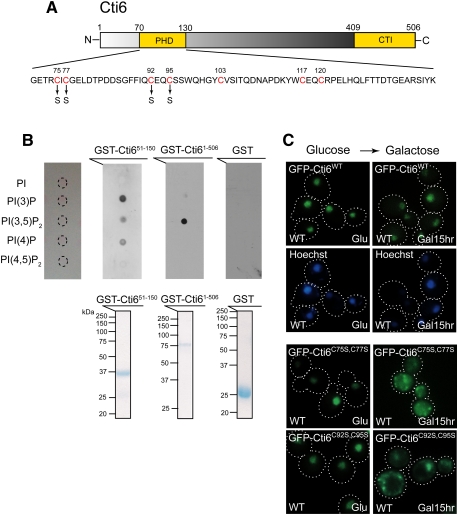
Figure 4.
Cti6 binds PI(3,5)P2 lipid, and the Cys residues in Cti6's PHD domain are important for nuclear localization of Cti6 in Gal medium. (A) Cti6 contains a PHD domain and a CTI domain. The PHD domain contains several Cys residues (red) that are potentially involved in zinc binding and important for PIP binding. Two Cti6 mutants were generated, such as Cti6C75S,C77S (Cys75–Cys77 → Ser75–Ser77) and Cti6C92S,C95S (Cys92–Cys95 → Ser92–Ser95). (B, top panel) Full-length Cti6 bound PI(3,5)P2 with high specificity, while the region (amino acids 51∼150) encompassing the PHD domain of Cti6 bound PI(3)P, PI(3,5)P2, and PI(4)P. (Bottom panel) Bacterially expressed GST fusion proteins were purified, and the same amounts of proteins were used for the protein–lipid overlay assay. (C) Wild-type Cti6 localized primarily in the nucleus in wild-type (WT) cells in both Glu and Gal media. The Cti6 mutants Cti6C75S,C77S and Cti6C92S,C95S localized in the nucleus in wild-type cells in Glu medium, but a significant portion of the mutant Cti6 proteins accumulated in the cytoplasm upon Gal shift.