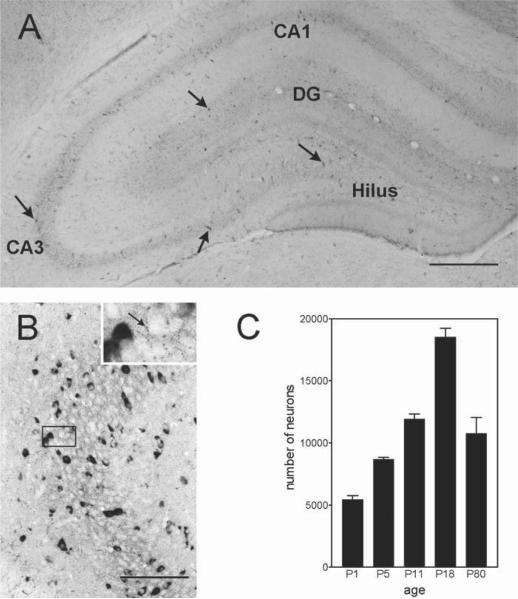
Fig. 2.
Expression pattern of CRH-secreting neurons in the hippocampal formation. (A) CRH-expressing neurons (arrows) are particularly common in the principal cell layers of the hippocampus, as shown in the immunocytochemistry photomicrograph from an 18-d-old rat. (B) CRH-expressing cells are interneurons as evident from the robust expression of GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase, the GABA-synthesizing enzyme), seen as dark signal in the in situ hybridization reaction. These CRH-expressing interneurons form “baskets” of processes around the cell bodies of the pyramidal cells (inset), innervating them directly. The age-dependent profile of CRH-expressing cells in the hippocampus is shown in panel (C). Total numbers of CRH neurons increase progressively from P1 to P18, with a subsequent decline to adult levels. Scale bar = 700 μm for A, 150 μm for B, and 50 μm for inset.