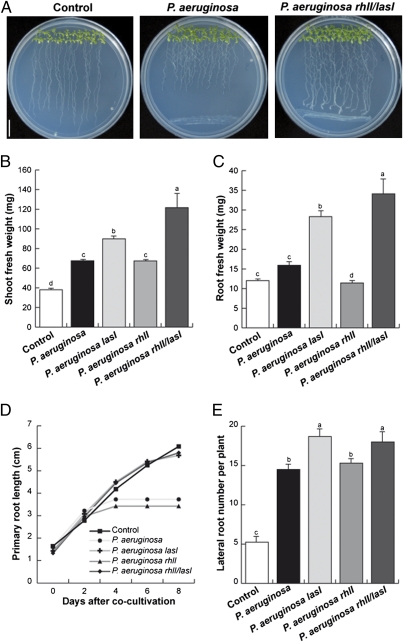
Fig. 1.
Effect of cocultivation with P. aeruginosa WT and QS mutant strains on root development and plant growth promotion. Four-day-old A. thaliana seedlings were cocultivated with WT P. aeruginosa or mutants defective on the AHL synthases LasI, RhlI, or LasI/RhlI at a distance of 5 cm from the primary root tip, and grown for an additional 8-d period. (A) Representative photographs of axenically grown Arabidopsis seedlings or seedlings cocultivated with WT P. aeruginosa and P. aeruginosa rhlI/lasI double mutant. (Scale bar = 1 cm.) (B) Effect of bacterial cocultivation on shoot biomass production or (C) root biomass production. Data from B and C show the means ± SD from three groups of 30 seedlings. (D) Effect of bacterial cocultivation on Arabidopsis primary root growth. Day 0 indicates the length reached by the primary root at the moment of bacterial application. Mean ± SD values were plotted at the indicated days in the kinetic experiment (n = 30). (E) Effect of bacterial cocultivation on lateral root formation. Date points represent mean ± SD (n = 30). These analyses were repeated three times with similar results. Different letters indicate means statistically different at P < 0.05.