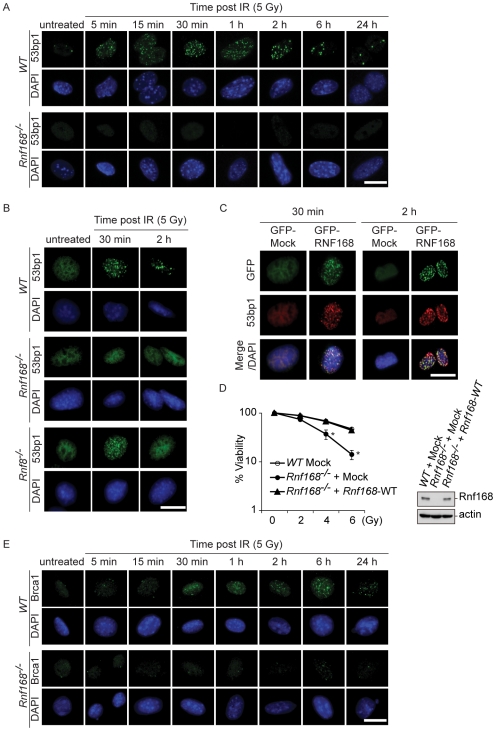
Figure 2. Rnf168 is required for the recruitment of 53bp1 to DNA damage sites.
(A) Representative micrographs of MEFs stained with anti-53bp1 antibody and DAPI. Rnf168−/− and WT MEFs were untreated or exposed to 5 Gy of IR and fixed at the indicated time post IR. Bars, 20 µm. (B) Representative micrographs of MEFs stained with anti-53bp1 antibody and DAPI are shown. Rnf168−/−, Rnf8−/− and WT MEFs were untreated or exposed to 5 Gy of IR and fixed at the indicated time post IR. Three independent experiments were performed. Bars, 20 µm. (C) Recovery of 53bp1 IRIF formation in Rnf168−/− MEFs complemented with full length RNF168. Immortalized Rnf168−/− MEFs were mock-transfected or transfected with GFP-tagged RNF168 expression vectors and cultured for 24 hours. Cells were fixed at 1 hour post-IR (5 Gy) and processed for immunofluorescence staining with anti-53bp1 antibodies. Three independent experiments were performed. Bars, 20 µm. (D) Clonogenic assay was performed to examine radiosensitivity of Rnf168−/− MEFs complemented with exogenous Rnf168 (left panel). Expression level of Rnf168 is shown for the MEFs used for the clonogenic assay (right panel). Data shown is representative of three independent experiments and is presented as the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05. (E) Representative micrographs of MEFs stained with anti-Brca1 antibody and DAPI. Rnf168−/− and WT MEFs were either untreated or exposed to 5 Gy of IR and fixed at the indicated time after IR. Bars, 2 µm.