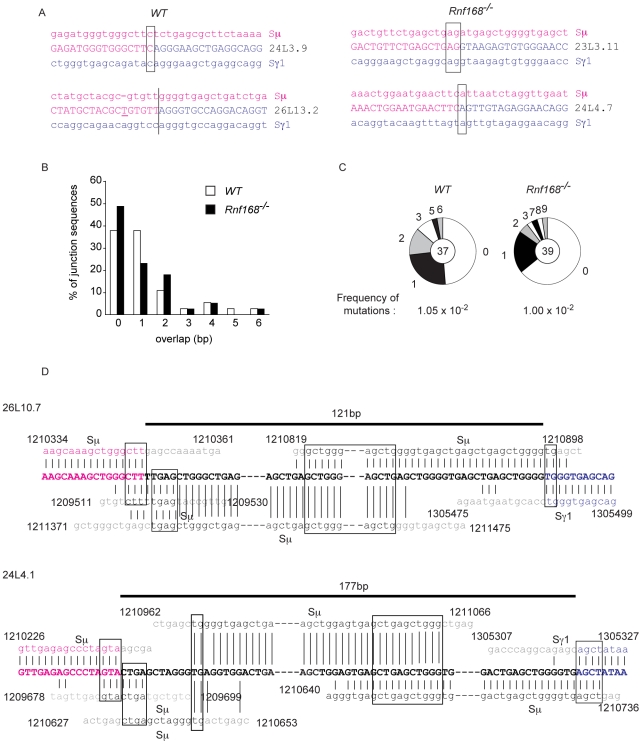
Figure 6. Analysis of the effect of Rnf168 inactivation on Sμ-Sγ1CSR junctions.
(A) Analysis of Sμ-Sγ1 CSR junctions. Overlap was determined by identifying the longest region at the switch junction of perfect uninterrupted donor/acceptor identity. No significant differences were observed. Representative data are shown from more than thirty clones in three independent experiments. (B) Purified splenic B cells were stimulated with LPS and IL-4 for 4 days. Genomic DNA was amplified by PCR and Sμ-Sγ1 junctions were sequenced. The percentage of junctions with the indicated nucleotide overlap is indicated (37 sequences from three WT mice and 39 sequences from three Rnf168−/− mice were analyzed). (C) Mutations in B-cells stimulated with LPS plus IL-4 for 4 days. Mutations near the Sμ-Sγ1 junctions (±50 bp) and frequencies of mutations are shown (37 sequences from three WT mice and 39 sequences from three Rnf168−/− mice were analyzed). The numbers of observed mutations are indicated in the periphery of the circular charts. (D) Sμ/Sγ1 junctions with unusual insertions obtained from Rnf168−/− B-cells. Sμ/Sγ1 sequences are shown in bold. The Sμ and Sγ1 [NT_114985.2 (strain 129/SvJ)] germline sequences are shown above or below each junction sequence. Lower-case letters indicate insertions. (|) indicates identity between nucleotides. Homology at the junctions is boxed. Two clones, 26L10.7 and 24L4.1, were obtained from independent experiments. 37 sequences from three WT mice and 39 sequences from three Rnf168−/− mice were analyzed.