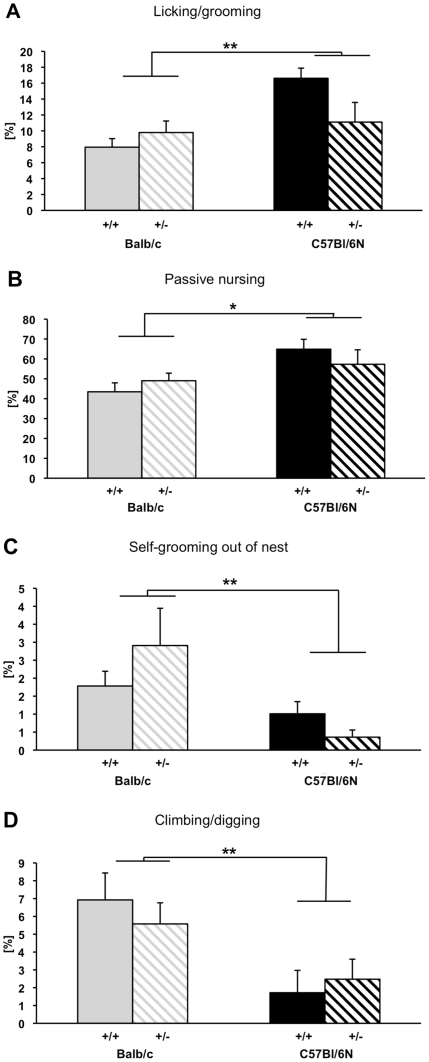
Figure 1. Effects of strain and genotype on maternal care behavior.
Behavioral strain differences between C57BL/6N and Balb/c mothers with a glucocorticoid receptor wildtype (GR +/+) or a heterozygous deletion (GR +/−) are exemplarily presented for four different behavioral measures: (A) ‘licking/grooming’, (B) ‘passive nursing’, (C) ‘self-grooming out of nest’ and (D) ‘climbing/digging’. While strains were found to differ significantly in all four measures, GR genotype did not affect the behavior. Moreover, a significant strain-by-genotype-interaction was found with respect to ‘licking/grooming’. While C57BL/6N +/+ dams spent more time ‘licking/grooming’ than Balb/c mothers of both GR genotypes, no difference was found between C57BL/6N +/− mothers and Balb/c dams. Data are presented as untransformed means ± standard error of the mean, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.