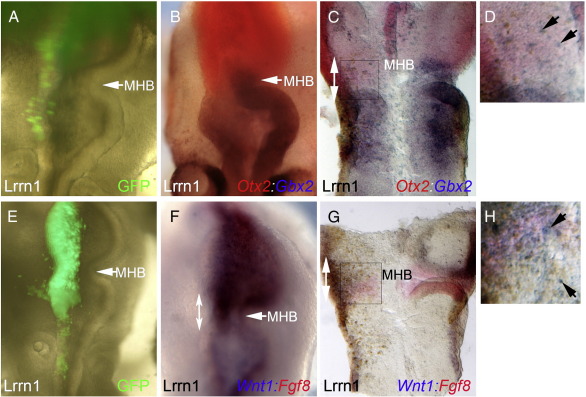
Fig. 4.
Ectopic expression of Lrrn1 across the MHB causes mixing at gene expression borders and a shift in the MHB. (A–H) Electroporation of Lrrnl-IRESGFP across the MHB interface (A) Overlay of Lrrnl-IRESGFP fluorescence reveals the position of electroporated cells. (B–D) In-situ hybridisation of Otx2 (red) and Gbx2 (blue). (B) The MHB morphological constriction and the expression border of Otx2 and Gbx2 are shifted caudally on the electroporated left hand side as compared to the control side (C) Flatmount preparation confirms the shift in expression of Otx2 and Gbx2 (white double arrow). (D) High magnification of box in C reveals mosaic expression of Obc2 and Gbx2 within anterior hindbrain (arrows). (F–H) In-situ hybridisation of Fgf8 (red) and Wntl (blue). Wntl marks anterior MHB in midbrain (Otx2-positive) cells FgfB marks posterior MHB in hindbrain (Gbx2-positive) cells (E) Overlay of Lrrnl-IRESGFP fluorescence. (F) Wntl expression extends caudally into anterior hindbrain on the electroporated left hand side as compared to control contra-lateral side (white double arrow) (G) The border of expression between Fgf8 and Wntl is fuzzy on the electroporated side (white double arrow). (H) High magnification of box in G reveals that Wntl-positive cells mix with Fgf8-positive cells and extend ectopically into the hindbrain (arrows). MHB: midbrain-hindbrain boundary.