Figure 8. Myometrial  model.
model.
The calcium- ( ), voltage- (V) and time-dependent kinetics for the two types of
), voltage- (V) and time-dependent kinetics for the two types of  currents,
currents, 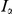 and
and 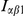 , are developed with experimental data from cloned mammalian myometrial and smooth muscle MaxiK
, are developed with experimental data from cloned mammalian myometrial and smooth muscle MaxiK  and
and 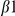 subunits expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes [63], [64]; the current density and proportion of
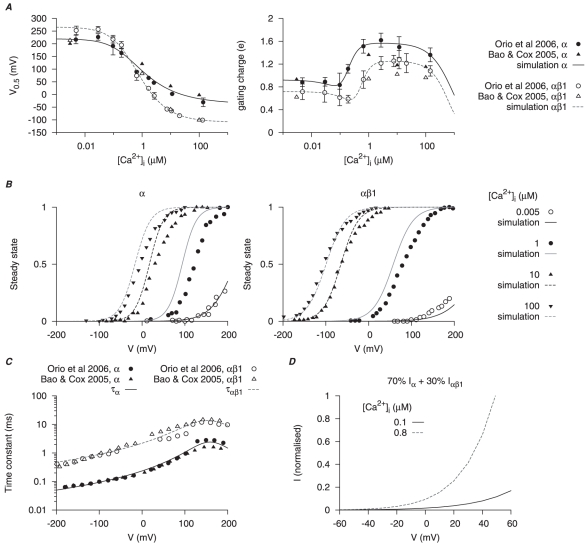
subunits expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes [63], [64]; the current density and proportion of 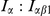 are adjusted with I–V relationships from different mammalian myometrial cells [17], [65], [66]. In A and C, solid and empty circles are experimental data for
are adjusted with I–V relationships from different mammalian myometrial cells [17], [65], [66]. In A and C, solid and empty circles are experimental data for 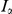 and
and 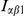 respectively. A,
respectively. A, 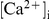 -dependent half-activation (
-dependent half-activation (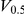 ) and activation gating charge. B, simulated activation steady-states for
) and activation gating charge. B, simulated activation steady-states for 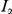 and
and 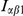 at different
at different 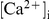 ; solid and empty circles are experimental data from Orio et al., [64] and Bao & Cox [63] respectively. C, V-dependent activation time constants for
; solid and empty circles are experimental data from Orio et al., [64] and Bao & Cox [63] respectively. C, V-dependent activation time constants for 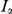 and
and 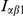 . D, simulated I–V relationships of
. D, simulated I–V relationships of 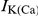 at anticipated myometrial resting and peak
at anticipated myometrial resting and peak 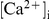 levels, with the proportion of
levels, with the proportion of 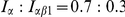 . Both I–V relationships are normalized to
. Both I–V relationships are normalized to 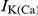 at
at 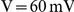 at peak
at peak 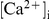 level.
level.