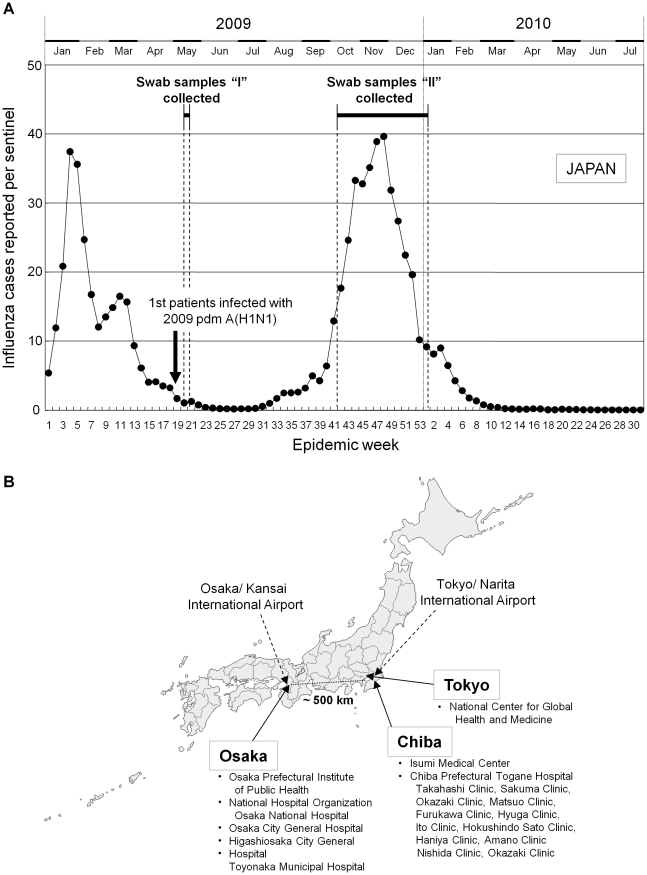
Figure 1. Collection of swab samples during initial and pandemic periods in Japan.
(A) The number of influenza cases reported per sentinel provider in Japan and the collection of swab samples from outpatients in Osaka, Tokyo, and Chiba areas. Swab samples were collected during initial and pandemic periods that are indicated by “I” (May 16 to May 20, 2009) and “II” (October 13, 2009 to January 6, 2010), respectively. In Japan, the first patients (three Japanese men) infected with the 2009 pdm A(H1N1) were discovered on May 9 (week 19), 2009. Data on the number of influenza cases reported per sentinel provider in Japan are acquired from the pandemic influenza A(H1N1) situation report of the Infectious Disease Surveillance Center. The number of sentinel clinics and hospitals is dependent on the relative population of each public health center's jurisdiction and in consideration of enabling comprehension of the incidents within each entire prefecture. The influenza sentinel points thus comprise approximately 3,000 pediatric hospitals/clinics and 1,800 internist hospitals/clinics in Japan. (B) Mapping of the hospitals, clinics, and public health institutes that contributed to our collection of swab samples from influenza patients. Osaka area: Osaka Prefectural Institute of Public Health, National Hospital Organization Osaka National Hospital, Osaka City General Hospital, Higashiosaka City General Hospital, and Toyonaka Municipal Hospital. Tokyo area: National Center for Global Health and Medicine. Chiba area: Isumi Medical Center, Chiba Prefectural Togane Hospital, and its associated clinics. The distance between Osaka and Tokyo/Chiba is approximately 500 km, and an international airport is located in each of these areas.