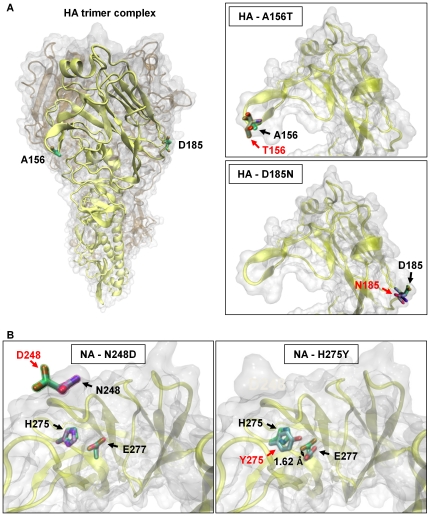
Figure 5. Structural modeling for HA and NA proteins with observed mutations.
(A) The left panel depicts the three-dimensional structure of an HA trimer complex deduced from the crystal structure of the H1N1 hemagglutinin of the 2009 A(H1N1) virus (PDB entry: 3LZG) to highlight one HA monomer with the amino acid substitutions (A156T and D185N) found in our severe cases. The right panels represent close-up views of the head part of the HA monomer with an amino acid substitution of A156T (top) or D185N (bottom). Both A156T and D185N substitutions appear to occur in the Ca antigenic site and to head outside the receptor-binding site. (B) Two model structures of NA created from the crystal structure of N1 neuraminidase (PDB entry: 2HU4). The left panel shows the NA protein with the N248D substitution, representing locations of the amino acid substitution as well as H275 and E277. Substitution of N248 to D248 appears to have little effect on the side chain of E277. The right panel shows the NA protein with the H275Y substitution, revealing that the side chain of E277 is shifted by 1.62 Å in the oseltamivir-resistant variant found in samples “II.”