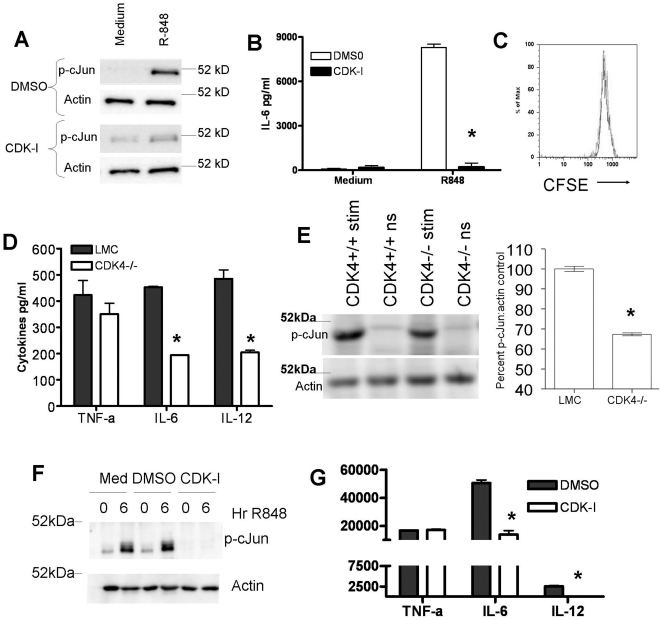
Figure 3. Effects of CDK4 inhibition on cytokine production and cJun phosphorylation in non-dividing cells.
Differentiated BMDCs were stimulated with the TLR7 agonist R848 in the presence and absence of CDK-I (SU9516) for 6 and 24 hours and monitored for A) cJun phosphorylation and B) IL-6 production, as described in Methods. C) As indicated by CFSE staining, matured BMDCs did not proliferate upon TLR7 stimulation – DCs were either fixed (light grey line) or stimulated with R848 for 48 hours (dark grey line) D) BMDCs from CDK4 deficient mice and CDK4+/+ littermate controls were stimulated with R848 (1 ug/ml) for 24 hours and supernatants subjected to cytokine multiplex analysis. E) BMDCs from CDK4 deficient mice and CDK4+/+ were stimulated with R848 (1 ug/ml) for 6 hours and assayed for cJun phosphorylation. The level of c-Jun phosphorylation in the CDK4 sufficient cells, as determined by the p-c-Jun:actin ratio, was set to 100%. The level of p-c-Jun in CDK4 deficient cells was normalized to the 100%. F) Human monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated with or without R848 for 6 hours in the presence of medium, DMSO (drug diluent), or the CDK4-specific inhibitor CINK. Cell lysates were then prepared and analyzed by Western blot for the presence of phospho-cJun. Actin was measured as a loading control. G) Human monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated with or without R848 for 24 hours in the presence of DMSO, or the CDK4-specific inhibitor CINK. Supernatants were collected and analyzed for cytokines using multiplex technology. (*) indicates statistical significance – P-value <0.05 using Student t-test. These data are each representative of between 2 and 4 separate experiments.