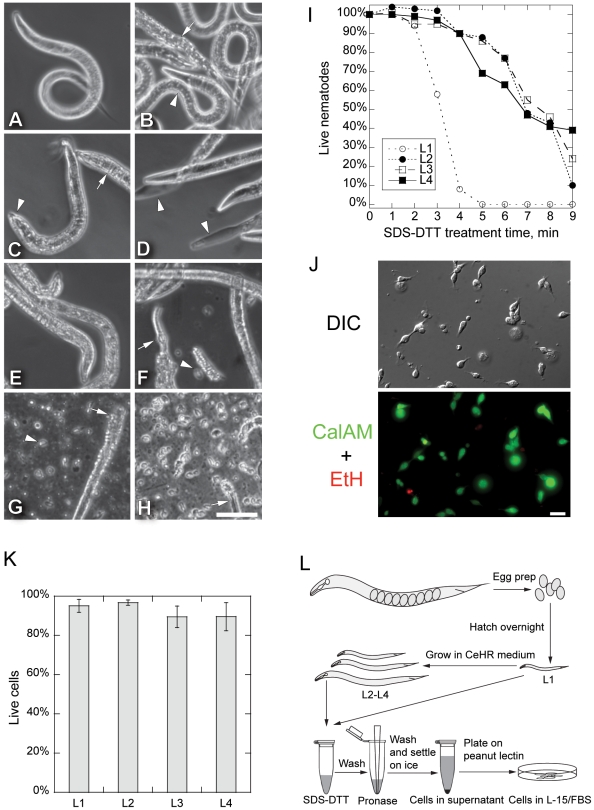
Figure 1. Larval Cell Isolation Procedure.
(A–H) Phase contrast micrographs of L3 nematodes during cell isolation. (A) Untreated L3 worms had smooth body outlines and normal bending motion. (B) Nematodes treated with 15 mg/ml pronase for 20 min did not dissociate during repeated pipetting. Most nematodes remained intact (arrowhead), but some developed a rougher cuticle (arrow). (C) Nematodes treated with SDS-DTT for 4 min remained intact. Treated nematodes swelled slightly, especially at the head (arrowhead), and cuticle wrinkles appeared (arrow). However, nematodes continued to move. (D) Longer SDS-DTT treatment (8 min) killed nematodes. Some showed cuticle regions devoid of cells (arrowheads). (E) A short 4 min SDS-DTT treatment followed by repeated pipetting in egg buffer alone did not dissociate nematodes. (F) Adding pronase after a short SDS-DTT treatment (4 min) began to digest the cuticle. By 10 min, some nematodes lost cuticle integrity and released cells (arrowhead). Arrow points to an exposed pharynx in a partially digested worm. (G) Repeated pipetting during pronase digestion of SDS-DTT treated (4 min) nematodes over 20 min completely digested most worms. More cells were released (arrowhead) with pipetting than without. Some partially digested worms remained (arrow). (H) After digested worms were settled for 30 min on ice, the supernatant mostly contained cells and little nematode debris (arrow). Large worm debris but few cells settled into the pellet (not shown). Scale bar in A–H is 50 µm. (I) L2–L4 stage nematodes survived longer in SDS-DTT than did L1 nematodes. Nematodes were scored as dead if they were rigid without any bending activity or had dissolved leaving empty cuticles. Live/dead scores were normalized to worms incubated for 10 min in egg buffer (0 min). (J) DIC and fluorescence micrographs of live/dead cell assay of adherent larval cells one day after plating. Calcein-AM stains for live cells (green), and ethidium homodimer indicates dead cells (red). Scale bar: 10 µm. (K) Viability of adherent L1–L4 larval cells tested by Calcein-AM and ethidium homodimer staining one day after isolation. Error bar is SD of three observations (L1: n = 819; L2: n = 417; L3: n = 485; L4: n = 741). (L) Schematic diagram of larval cell isolation procedure. Eggs are isolated from gravid adults and hatched overnight. L1 larval cells are isolated immediately, while larvae are grown in CeHR medium for L2 to L4 stage cell isolation. Nematodes are treated with SDS and DTT for 2–4 min, washed with egg buffer, and incubated with pronase for 8–20 min with gentle pipetting. Cells were separated from debris by settling on ice for 30 min, plated onto penut lectin coated glass substrates and maintained in L-15/fetal bovine serum medium.