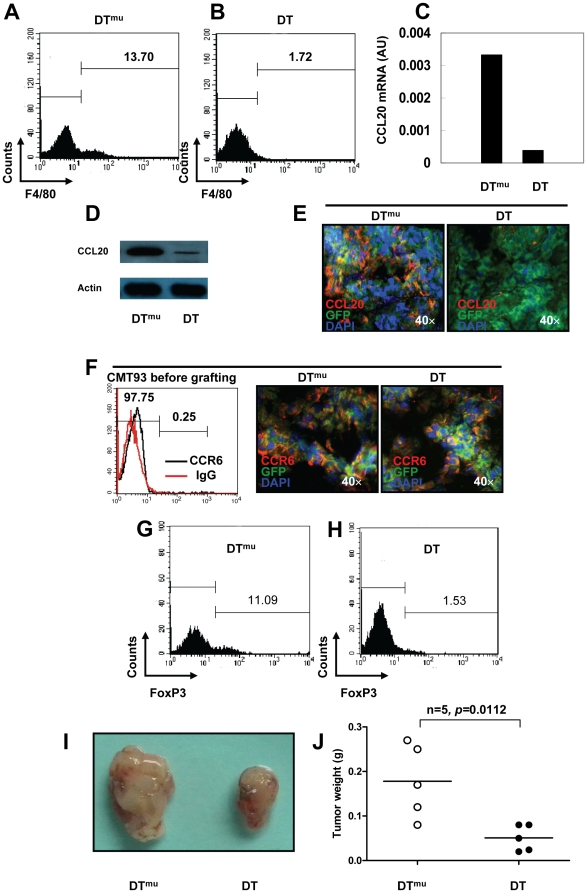
Figure 5. Conditional macrophage ablation disrupted Treg-cell recruitment and inhibited the growth of CRC in mice.
(A, B) Flow cytometric analysis of TAMs derived from grafted CRC in CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT. (C) CCL20 mRNA levels in grafted CRC in CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT (data from 5 mice of each group were pooled together). (D) Lysates of grafted CRC from CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT were subjected to western blotting for CCL20 expression. Actin - loading control. (E) Immunofluorescence staining with anti-mouse CCL20 was performed on cryosections of GFP+ CMT93 grafted tumor mass derived from CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT for 14 days. (F) Flow cytometric analysis of CCR6 expression for GFP+ CMT93 cells before grafting (left panel), and CCR6 staining on cryosections of GFP+ CMT93 grafted tumor mass derived from CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT for 14 days (middle and right panel). (G, H) Number of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Treg-cells in grafted CRC in CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT. (I) CRC grafted in CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT for 14 days. (J) Tumor weight of CRC grafted in CD11b-DTR mice injected with DTmu or DT for 14 days. Representative data are shown which had been reproduced in 2 independent experiments.