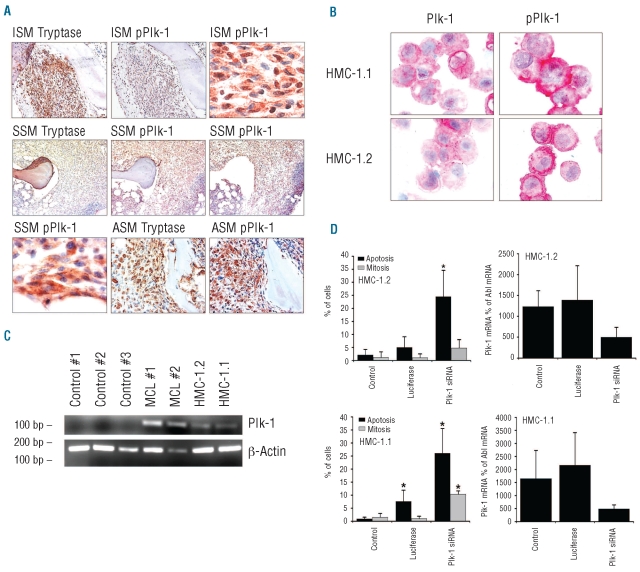
Figure 1.
Expression and functional role of Plk-1 in neoplastic mast cells. (A) Detection of tryptase, Plk-1, and phosphorylated Plk-1 (pPlk-1) in primary neoplastic mast cells (MC) in serial bone marrow sections from patients with indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM; patient #2 and #5 in Online Supplementary Table S1), smoldering systemic mastocytosis (SSM; patient #16 in Online Supplementary Table S1) and aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM; patient #11 in Online Supplementary Table S1) (magnification: right upper and left lower x100; all other images: x40). (B) Immunocytochemical detection of pPlk-1 and Plk-1 in HMC-1.1 cells and HMC-1.2 cells using antibodies against Plk-1 and pPlk-1 (magnification x100). Images were viewed under an Olympus BX50F4 microscope (Olympus, Hamburg, Germany) and prepared using an Olympus DP11 camera and Adobe Photoshop CS2 software version 11.0 (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA, USA) to adapt brightness and contrast. Staining protocols are described in the text. (C) RT-PCR analysis of expression of Plk-1 mRNA in mononuclear blood cells from three healthy controls (#1,#2,#3), bone marrow cells obtained from two patients with mast cell leukemia (MCL), HMC-1.1 cells and HMC-1.2 cells. (D) Effects of Plk-1 siRNA on mitosis and viability in HMC-1.2 cells (upper panel) and HMC-1.1 cells (lower panel). Left panels show the percentage of mitotic (gray bars) and apoptotic cells (black bars) after transfection with Plk-1 siRNA or luciferase siRNA. Right panels show siRNA-induced knockdown of Plk-1 mRNA assessed by quantitative PCR. Plk-1 mRNA levels are expressed as percent of Abl mRNA. Results represent the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments. Asterisk: P<0.05.