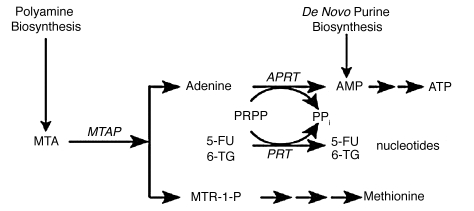
Figure 1.
MTAP metabolic pathway. In normal cells, MTAP cleaves MTA, a by-product of polyamine biosynthesis, into adenine and 5-methylthioribose-1-phosphate (MTR-1-P). Adenine is converted to AMP by the ubiquitous enzyme adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT), with phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) serving as donor of the phosphoribosyl group. MTR-1-P is converted by a series of steps to methionine. AMP is also produced in cells by de novo purine biosynthesis. In addition to APRT, other cellular phosphoribosyltransferases, such as hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase and orotate phosphoribosyltranferase, convert purines and pyrimidines to nucleotides.49