Figure 1.
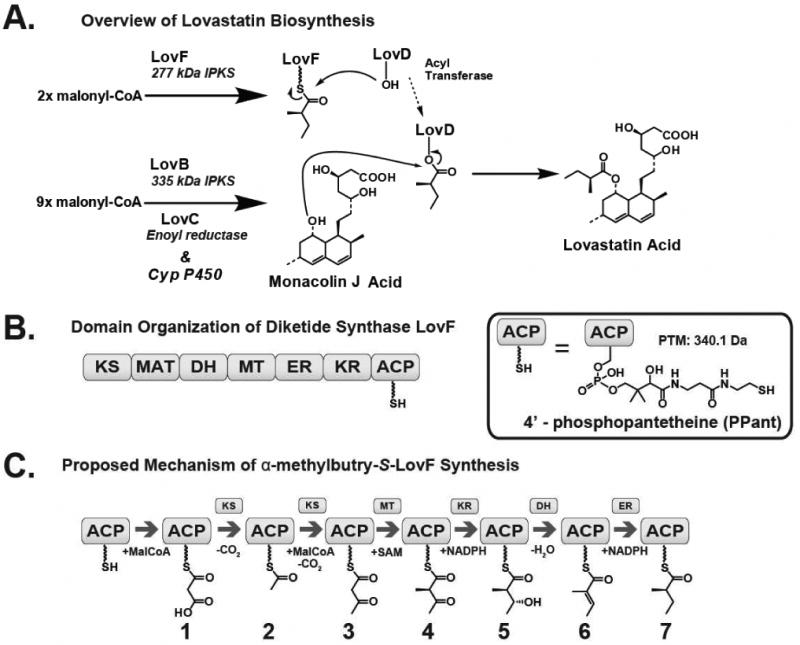
Biosynthesis of lovastatin. (A) Overview of the biosynthesis of lovastatin by LovB and LovF. LovD, a broadly acting acyl transferase, mediates the transfer of α-methylbutryate from LovF to the C8 hydroxyl position of monacolin J acid to form lovastatin acid. (B) LovF consists of multiple catalytic domains: β-ketoacyl synthase (KS), malonyl-CoA:ACP acyltransferase (MAT), dehydratase (DH), methyltransferase (MT), enoylreductase (ER), ketoreductase (KR), and acyl carrier protein (ACP). The 4′-phosphopantetheinylated ACP serves as a covalent tether for the acyl-intermediate as it is processed by the other catalytic domains of LovF (C) Based upon the catalytic domain composition of LovF, the enzyme is predicted to produce multiple covalent intermediates before biosynthesis of α-methylbutyrate.
