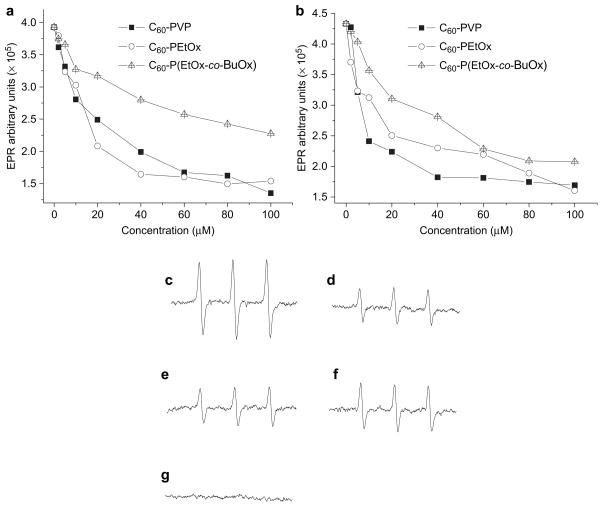
Fig. 5.
Dose-dependent superoxide scavenging by C60-polymer complexes as determined by EPR spectroscopy: (a) 0.025 mM HX and 10 mU XO were used as the superoxide source; (b) 0.02 mM FMN was used as the superoxide source. Representative EPR spectra: (c) HX + XO alone; (d) HX + XO in the presence of 100 μM in C60 of C60-PVP; (e) HX + XO in the presence of 40 μM in C60 of C60-PEtOx; (f) HX + XO in the presence of 100 μM in C60 of C60-P(EtOx-co-BuOx); (g) HX + XO in the presence of 400 U/ml SOD1. Each sample was incubated at r.t. for 5 min.