Figure 2. Affinity-purified anti-Neu5Gc IgG antibodies can specifically kill tumors expressing cell-surface Neu5Gc in vivo.
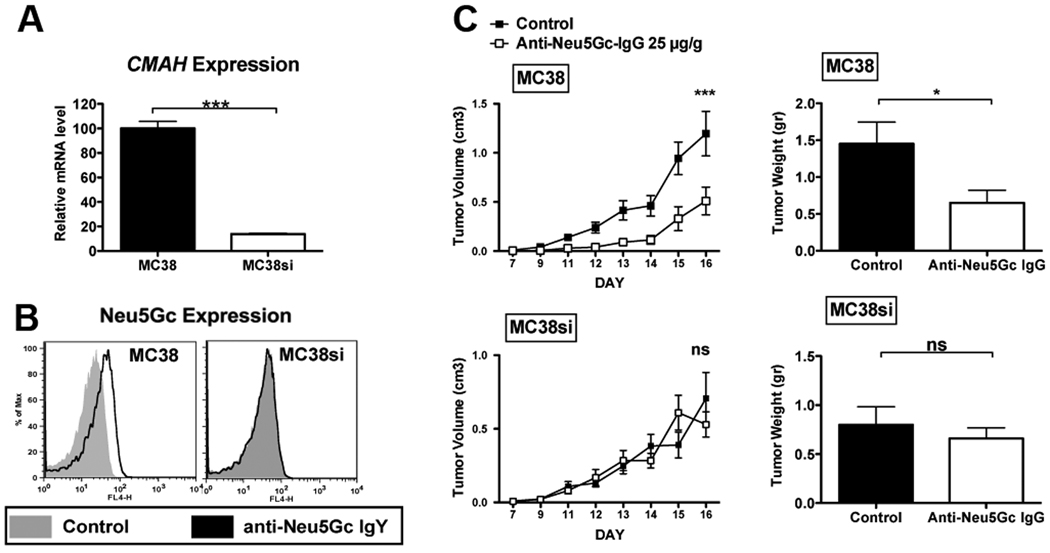
(A) qPCR reveals down regulation of CMAH gene expression in MC38 cells with siRNA to CMAH (MC38si) compared to the wild-type MC38 cells (mean±SD of triplicates; Two tailed unpaired t-test P<0.0001). (B) FACS analysis using a polyclonal chicken anti-Neu5Gc antibody confirms reduced expression of Neu5Gc on the cell surface (representative of two independent experiments). (C) Cmah−/− mice were injected subcutaneously with MC38 (right flank) and MC38si (left flank). Affinity-purified anti-Neu5Gc IgG can specifically kill tumors expressing Neu5Gc on the cell surface (MC38) (n=6) compared to the control-treated mice (n=5), but no significant effect is observed when the Neu5Gc expression on the cell surface is diminished (MC38si), as determined by daily measurements of tumor volumes (left panels; mean±SEM; Two-way ANOVA P<0.001) or terminal tumor weights on day 16 (right panels; mean±SEM; Two-tailed t-test * p=0.036), representative of 3 independent experiments. Direct comparison of the effects of anti-Neu5Gc IgG on these tumors in the same mice revealed attenuated MC38 tumors compared to the control MC38si tumors (P=0.0392, Two-way-ANOVA).
