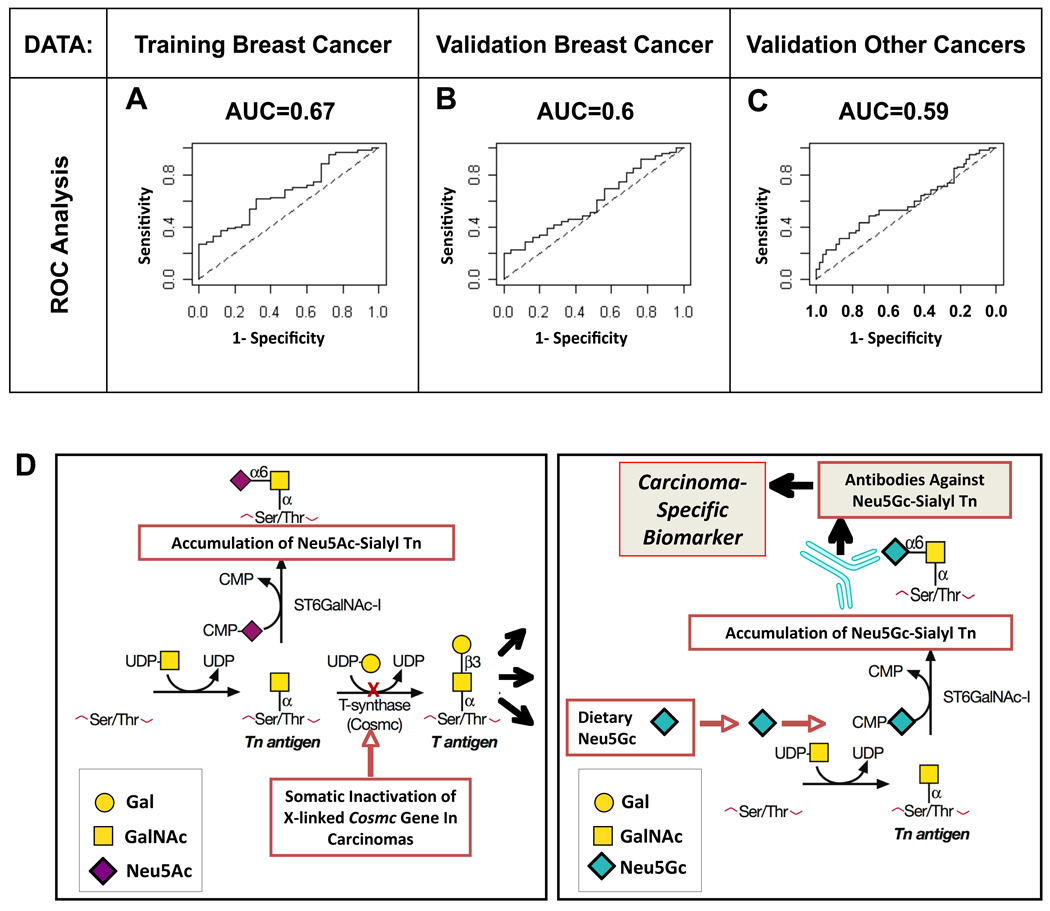
Figure 4. Anti-GcSTn is a classifier for cancer cases/controls and is suggested to be a human-specific and tumor-associated carcinoma biomarker.
Probabilities of being a cancer case were calculated using logistic regression where predictors were the two parameters, α and β, which summarized the anti-Neu5Gc antibody response to glycan 6 (Neu5Gc-sialyl-Tn; GcSTn) against the pan antibody level of 20 Neu5Ac glycans. (A) ROC curve for training data, used to select glycan 6, that had 67 non-metastatic breast cancer cases and 25 controls. (B) ROC curve for the first validation data set, which had 74 new non-metastatic breast cancer cases and 25 new controls. (C) ROC curve for a second validation data set, which had 99 cases of other cancer types and 55 controls. The biochemical and genetic rationale for the generation of the novel human carcinoma biomarker is schematically presented. (D) Somatic Cosmc mutations generate incomplete O-linked glycosylation, resulting in tumor-associated expression of the sialylated-Tn antigen in many carcinomas (left panel). Incorporation of dietary-Neu5Gc by such carcinomas generates Neu5Gc-sialyl Tn, detected by the humoral adaptive immune system as foreign, thus generating antibodies against it. Such xeno-auto-antibodies specific for Neu5Gc-sialyl Tn, are hypothesized to be novel biomarkers for early screening of carcinomas and/or potential immunotherapeutic tools (right panel).