Figure 5. CDC and ADCC of cells expressing cell surface GcSTn.
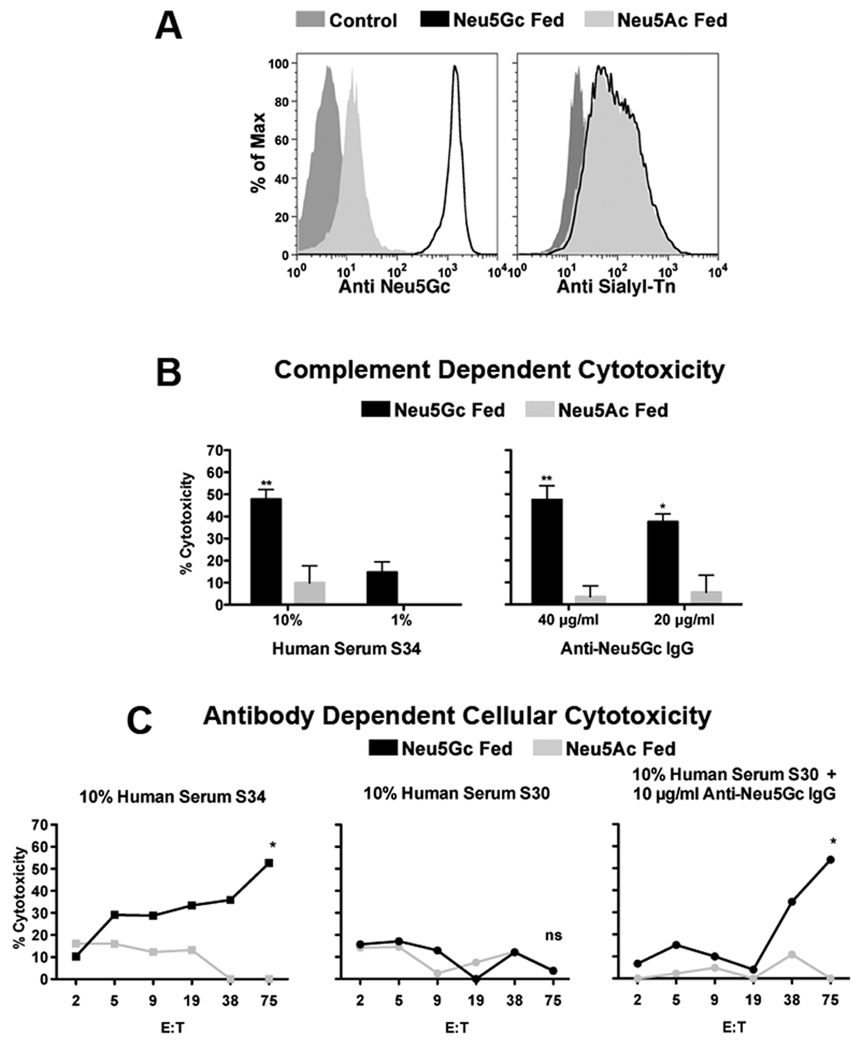
Jurkat cells were chased-out of pre-existing media-derived Neu5Gc then fed with 3 mM Neu5Ac or Neu5Gc. (A) FACS analysis using a polyclonal chicken anti-Neu5Gc antibody (highly specific to all Neu5Gc but not Neu5Ac glycans (32)) confirms feeding with Neu5Gc. A mouse monoclonal antibody specific for sialyl-Tn (STn) demonstrates cell-surface expression of this structure with either terminal Neu5Ac (STn; on Neu5Ac fed cells) or Neu5Gc (GcSTn; on Neu5Gc fed cells). (B) Human serum S34 (high in anti-GcSTn reactivity; Fig. 3B) can promote complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) of cells fed with Neu5Gc but not with Neu5Ac (left panel). Similarly, affinity-purified human anti-Neu5Gc IgG (high in anti-GcSTn reactivity; Fig. 1C) can promote CDC of Jurkat cells in a Neu5Gc-dependent manner (right panel; two independent experiments each; mean±SD; Two-way ANOVA, * P<0.01, ** P<0.05). (C) Human serum S34 (10%) can promote Neu5Gc-specific antibody-dependent cellular-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) with increasing effector:target ratios (target cells, T, Jurkat cell fed with Neu5Ac/Neu5Gc; effector cells, E, PBMCs in RPMI), in contrast to human serum S30 (10%) (5). However, when human serum S30 (10%) was supplemented with 10 µg/ml of the purified anti-Neu5Gc IgG it could promote ADCC similar to human serum S34 (representative of two independent experiments; two-way ANOVA * P<0.05).
