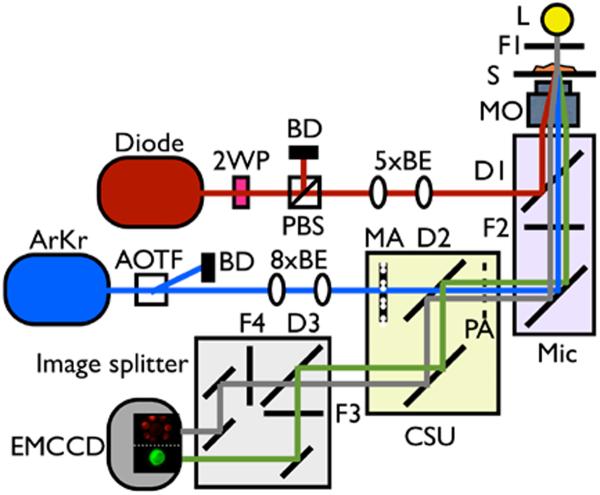
Figure 1.
Combined video-rate fluorescence confocal microscope and single beam laser tweezers system. The 1064 nm laser providing the ability to optically trap and manipulate cells is directly coupled into the back port of an inverted optical microscope and reflected towards the objective lens by an infrared-reflecting dichroic mirror. The spinning disk assembly is attached to the left side port of the microscope and the excitation light and fluorescence simply passes the dichroic mirror. 2WP is a half waveplate, 5×BE is a 5× beam expander, 8×BE is a 8× beam expander, AOTF is acoustic optical tuneable filter, ArKr is a multiline ArKr ion laser, BD is a beam dump, CSU is a confocal spinning unit, D1 is a 900 nm short pass dichroic mirror, D2 is a quad band dichroic mirror, D3 is a 560 nm long pass dichroic mirror, Diode is a 1064 nm CW diode laser, EMCCD a is electron multiplying charged coupled devise camera, F1 is a 620/30 nm bandpass filter, F2 is a 750 nm short pass dichroic, F4 is a 609/54 nm bandpass filter, F5 is a 525/50 nm bandpass filter, L is halogen lamp, Mic is the microscope, MA is a microlens array, MO is the microscope objective, PA is a pinhole array, PBS is a polarizing beam splitter, and S is sample.