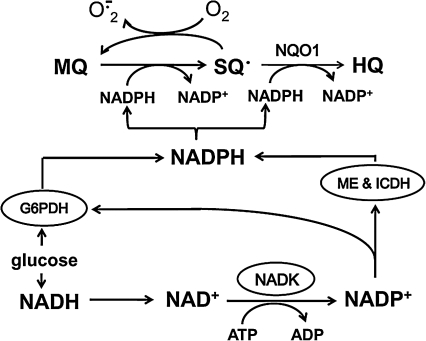
FIG. 1.
MQ metabolism through a one-electron reduction in MQ-SQ• redox cycling or NQO1-catalyzed two-electron reduction in MQ-to-HQ formation imposes a high demand on cellular NADPH supply. NADPH drain results in metabolic responses that support NADPH generation, such as the sacrifice of the NAD+/NADH redox pools in favor of NADP+ and NADPH generation and the stimulation of activities of NADPH-generating enzymes. MQ, menadione; SQ•, semiquinone radical; HQ, hydroquinone; NQO1, NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase, also known as DT diaphorase; O2•−, superoxide; G6PDH, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; ME, malic enzyme; ICDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; NADK, NAD kinase.