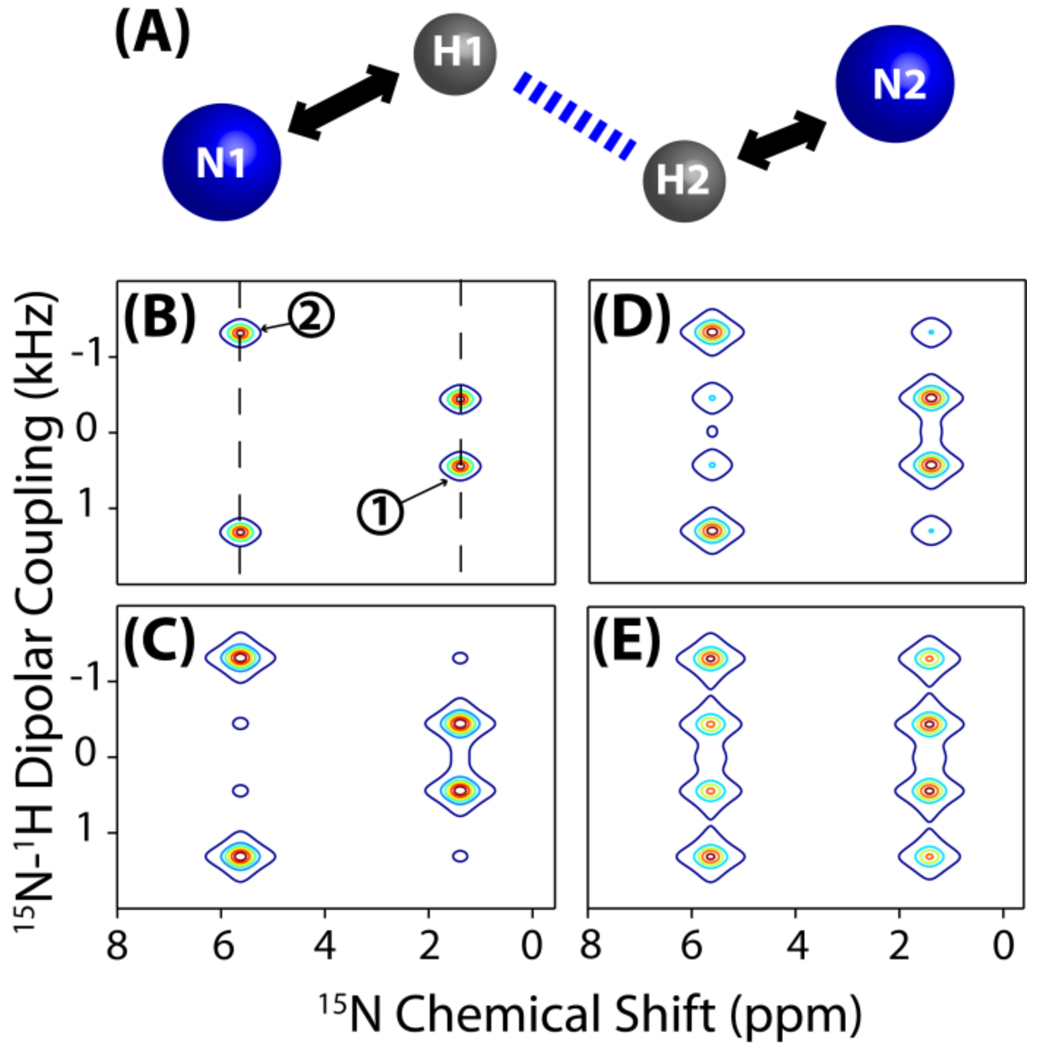
Figure 4. Simulations demonstrate the feasibility of resonance assignment by the PELF-mix pulse sequence.
PELF-mix may be used on aligned, uniformly labeled samples for resonance assignment. (A) The spin system used in the simulation includes a weakly dipolar coupled (N1 and H1) and a strongly dipolar coupled (N2 and H2) N-H pairs. Simulated PELF-mix spectra of this spin system are presented for tmix=0 ms (B), 5 ms (C), 15 ms (D), and 30 ms (E). In (B), dashed diagonal lines are drawn to indicate the N1-H1 and N2-H2 pair dipolar splittings on the PELF-mix spectra. The dipolar coupling between N1 and H1 was set to be 0.89 kHz during the frequency encoding t1 period and about 1.49 kHz during the z-magnetization transfer from proton to 15N nuclei during the spin-lock using the WIM pulse sequence. The dipolar coupling between N2 and H2 was set to be 2.68 kHz during the frequency encoding period and about 1.49 kHz during the WIM period. During the spin diffusion period (tmix), the proton-proton dipolar coupling between H1 and H2 was set to be 245 Hz.