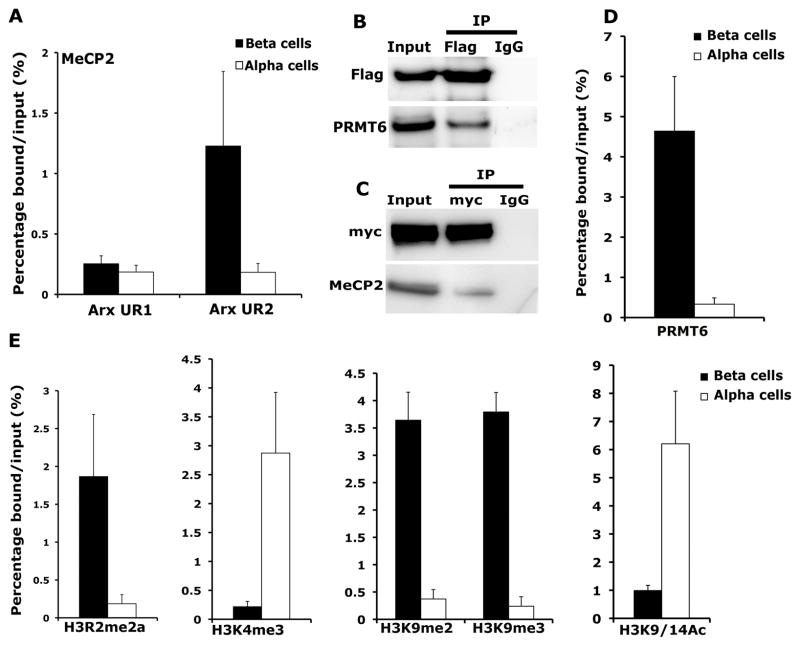
Figure 4. MeCP2 binds to the Arx locus in beta cells and recruits H3R2 methyltransferase PRMT6 to repress Arx expression.
(A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis showing the binding of MeCP2 to the two CpG rich regions, UR2 (−2111 to −1960) and UR1 (−184 to −254) of the Arx locus in beta and alpha cells. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis examining the interaction of MeCP2 and PRMT6. Cell extracts from Min6 cells transfected with Flag-MeCP2 construct were used as input for immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Flag antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with Flag and PRMT6 antibodies. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis for the interaction of PRMT6 with MeCP2 using immunoprecipitation with myc-tag antibody on Min6 cells transfected with myc-PRMT6 construct, and Western blotting with myc-tag and MeCP2 antibodies. (D) ChIP analysis comparing the recruitment of PRMT6 to the UR2 region of Arx locus in beta and alpha cells. (E) ChIP analysis comparing the levels of asymmetric H3R2 di-methylation (H3R2me2a), H3K4 trimethylation (H3K4me3), H3K9 di- and tri-methylation (H3K9me2 and H3K9me3) and H3K9/14 acetylation (H3K9/14Ac) at the differentially methylated UR2 region of the Arx locus in beta and alpha cells purified from 5 months old wildtype mice. These analyses indicate enrichment of histone modification associated with repression of gene expression, namely, H3R2me2a, H3K9me2 and H3K9me3 at the Arx locus in pancreatic beta cells. The error bars represent standard error (SEM) of the mean. See also Figure S4.