Figure 5.
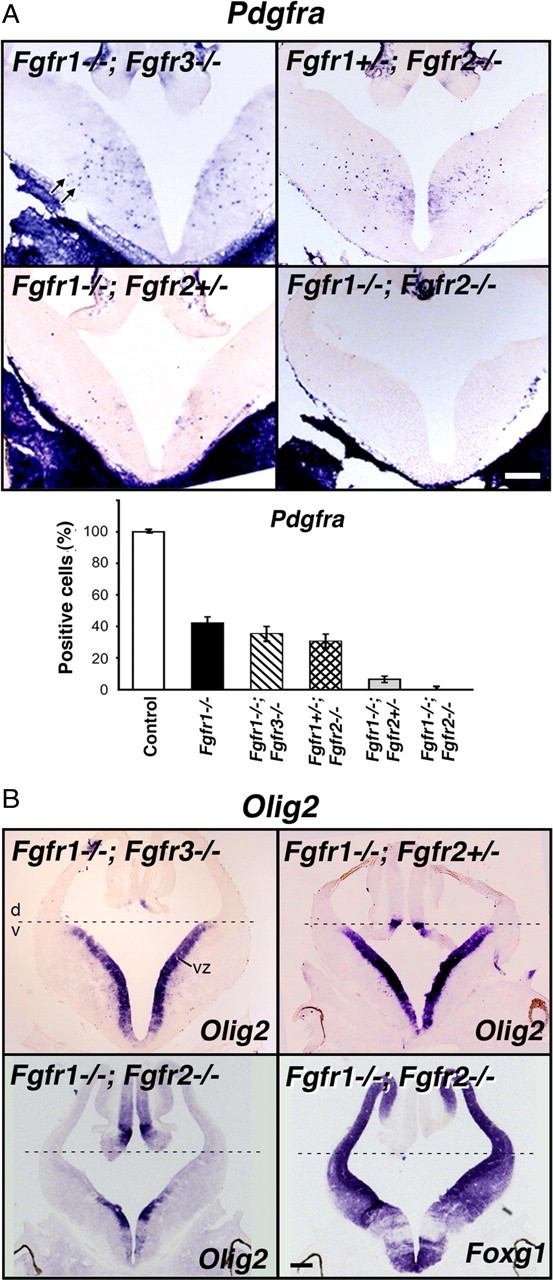
Fgfr1 and Fgfr2 gene dosages govern the extent of OL progenitor induction. Coronal sections of E12.5 forebrain from control or mutants with different combinations of the three receptors deleted (Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr3−/−, Fgfr1+/−;Fgfr2−/−, Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2+/−, Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2−/−) were analyzed by in situ hybridization for the expression of Pdgfra (A), Olig2 and Foxg1 (B) mRNA. Three to four matched sections, each from three to four mice, were analyzed from each group. A, Compared with the controls in mice lacking Fgfr1 in combination with one or both alleles of Fgfr2, but not of Fgfr3, the numbers of Pdgfra+ OLPs (arrows) were dramatically reduced (Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2+/−) or totally failed to develop (Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2−/−). Error bars represent SEM (N = 3–4). B, Dorsal–ventral (d, v) patterning, shown by the expression of Olig2 in the ventral VZ, remained intact in all mutants except in the Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2−/− double mutant. Foxg1 and Olig2 expression patterns are shown in serial sections in these mutants to demonstrate the loss of Olig2 expression from the regions of the ventricular zone corresponding to regions of strong Foxg1 expression (in which floxed Fgfr1 and Fgfr2 genes should be deleted by Foxg1-cre), but as expected, Olig2 remained in the regions mostly negative for Foxg1. Scale bars, 200 μm. Note the severe failure of Pdgfra+ OLPs to develop in Fgfr1−/−;Fgfr2+/− mutants without disruption of d-v patterning.
