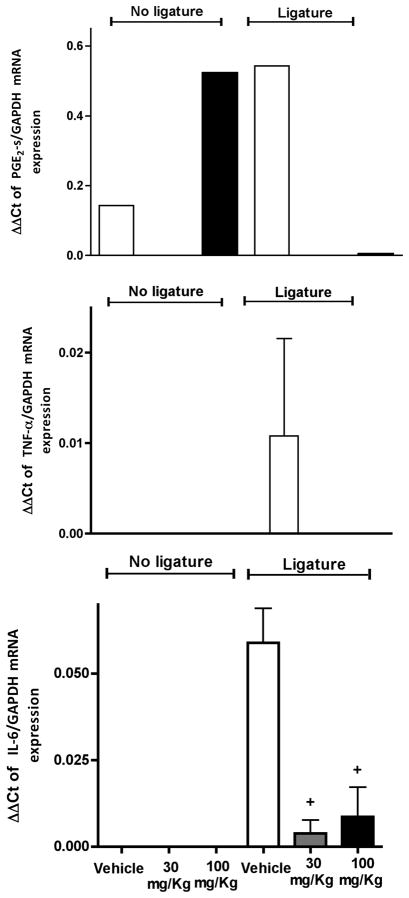
Figure 5.
Curcumin inhibits cytokine gene expression in experimental periodontitis. In the absence of periodontal disease, only PGE2-synthase mRNA was significantly induced by the higher dose of curcumin in the absence of ligature-induced periodontal disease. The animals were treated with 30 or 100 mg/Kg of curcumin by oral gavage daily for 15 days. Control animals received the same volume of the vehicle by oral gavage. Cotton ligatures were placed around the first molars of rats bilaterally to induce periodontal disease. After 15 days, the animals were sacrificed and total RNA was isolated from gingival biopsies with (‘Ligatures’) and without (‘No ligatures’) periodontal disease and used for RT-qPCR performed with pre-designed primers and probes for the indicated target genes and to the housekeeping GAPDH using TaqMan reagents. The results were analyzed by the delta-Ct method and expression of target genes was normalized to GAPDH expression. (+) indicates significant reduction (p< 0.05) in comparison to vehicle control with ligatures. Bars indicate means and vertical lines standard error of mean of at least three animals in each experimental group, except for PGE2-s mRNA analysis in which the samples of three animals in each experimental group were pooled to enable detection and there are no error bars.