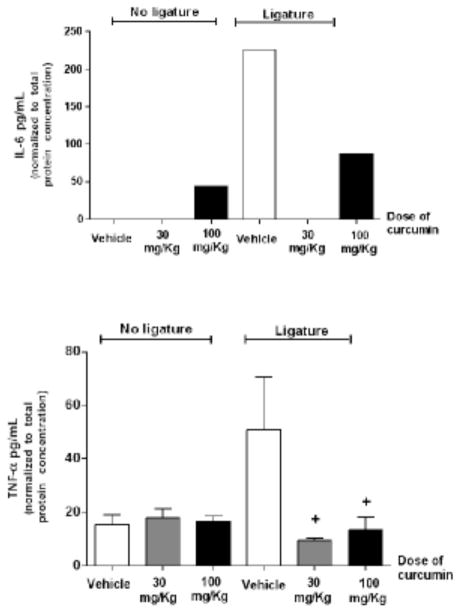
Figure 6.
Effective inhibition of both IL-6 and TNF-α production in periodontally diseased tissues by curcumin. In the absence of ligatures, the higher dose of curcumin was associated to increased production of IL-6, whereas TNF-α production was not affected. Gingival tissues around both lower first molars with (‘Ligature’) and without (‘No ligature’) experimentally induced periodontal disease were collected after 15 days of administration of curcumin (30 or 100 mg/Kg) by oral gavage. Control animals received the same volume of vehicle. Total protein was extracted and used in ELISA tests to quantify the expression of the target cytokines. These tests were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions and the results for each sample were normalized to the concentration of total proteins determined by a Lowry-based microassay (DC assay, Bio-Rad). (+) indicates significant difference (p< 0.05) in comparison to vehicle control in animals with ligature-induced periodontitis. Bars indicate means and vertical lines standard error of mean of at least three animals in each experimental group. IL-6 concentration was determined in pooled samples from three animals in each experimental group due to the low level of expression, and the bar indicate the average of the triplicate measurement from these pooled samples.