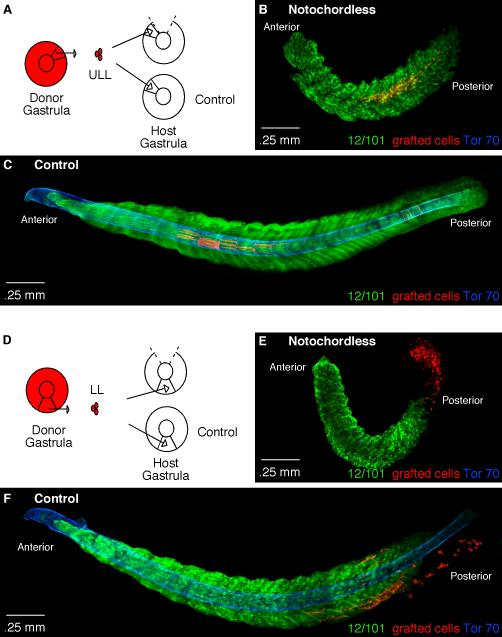
Figure 4. The role of the notochord on the axial positioning of myotome fibers.
(A) A diagram depicting homotopic grafts performed to the upper lateral lip-ULL region in control and notochordless gastrulae. (B) A stage 25 notochordless embryo containing RDA-labeled cells from the ULL (red) that formed myotome fibers in the central region of somites. The notochordless embryo is stained for 12/101 (green) to show myotome formation and Tor-70 (blue) to confirm the absence of the notochord. (C) A control stage 25 embryo containing ULL cells (red) that have formed myotome fibers shown by the muscle-specific antibody 12/101 (green) positioned at the level of the notochord as shown by Tor-70 staining (blue). (D) A diagram depicting homotopic grafts performed to the lower lip-LL region in control and notochordless gastrulae. (E) A stage 25 notochordless embryo with LL-grafted cells (red) stained with the muscle-specific antibody 12/101 (green) and Tor-70 (blue) to confirm the absence of the notochord. (F) A control stage 25 embryo stained with 12/101 (green) and Tor-70 (blue) containing LL-grafted cells (red) that have begun to form myotome fibers mostly in the dorsal and ventral aspects of posterior somites.