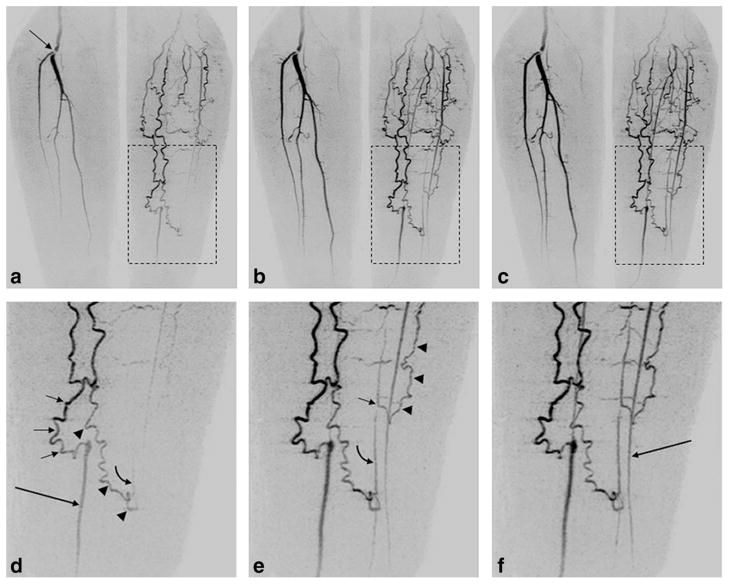
FIG. 8.
Illustration from a patient study of the spatial and temporal resolution of Max CAPR (4.9-sec acquisition time). a–c: Coronal MIPs of consecutive 4.9-sec timeframes in a patient having a lesion at the origin of the right popliteal bifurcation (arrow, (a)) and filling via collateral vessels of the vasculature of the left leg. d–f: Enlargements from the region of the left leg (dashed boxes, (a–c)), allowing delineation of the filling patterns. d: Filling of the native distal left posterior tibial artery (long arrow, (d)) is done via a medial collateral vessel (short arrows, (d)). Second collateral vessel (arrowheads, (d)) spontaneously anastomoses to a distal native peroneal artery, with an early hint of retrograde flow (curved arrow, (d)). e: Subsequent frame shows further retrograde flow along peroneal artery (curved arrow, (e)), as well as a more proximal anastomosis in the peroneal artery (short arrow, (e)) from a third collateral vessel (arrowheads, (e)). f: Next frame shows further enhancement, including filling of native left anterior tibial artery (long arrow, (f)). See also Supplementary Videos V3 and V4.