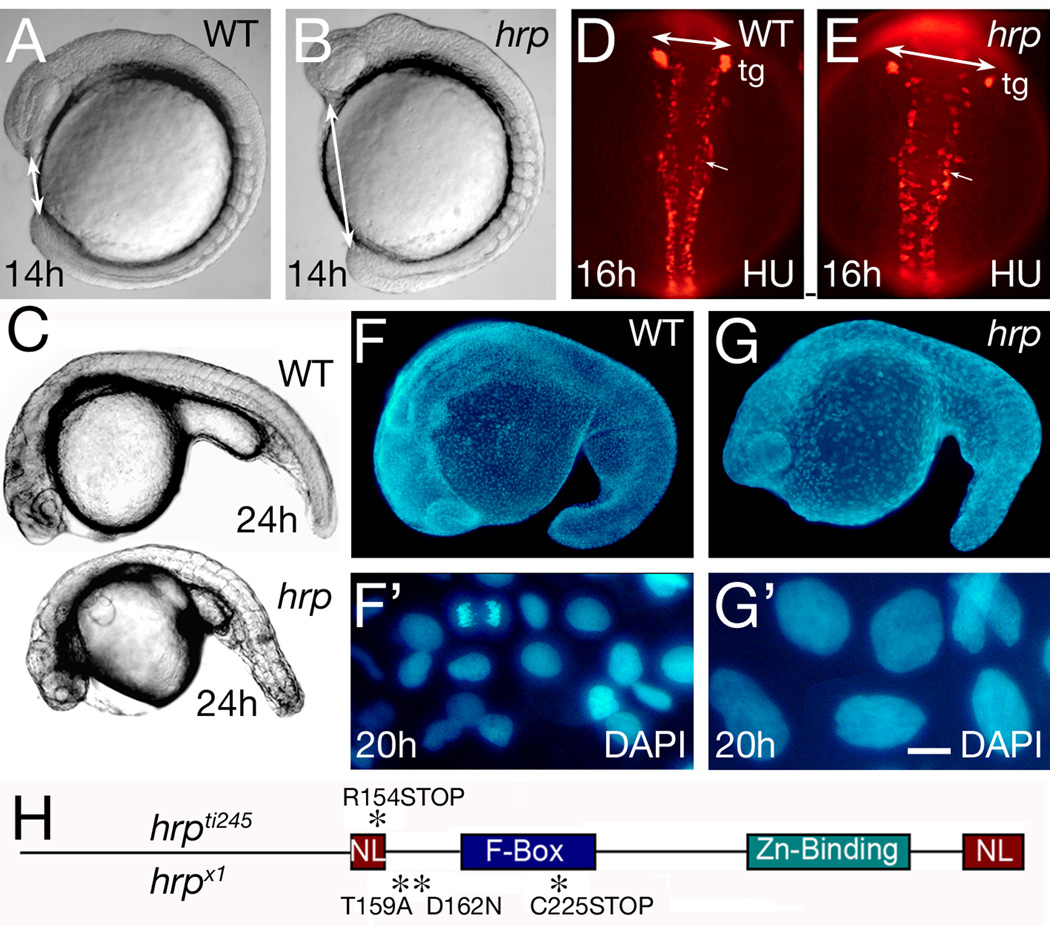
Fig. 1. General phenotype of harpy mutants.
(A, B) Live wild-type and mutant embryos at the 10 somite stage. Double sided arrows indicate the distinctive nose-tail bud separation in the mutants.
(C) Side views of live wild-type and mutant embryos at 24 hours.
(D, E) Anti-HuC (HU) stained neurons at 16 hours in wild-type and mutant embryos. The trigeminal ganglia (tg) are indicated, and double sided arrows indicate the width of the neural keel. Small arrows indicate single cells; note the larger size of the mutant cells.
(F, G) DAPI-staining at 20 hours in wild-type and mutant embryos. F’ and G’ are whole embryo dissociations. Note the cell in mitosis in the WT field; no cells are found in mitosis in the mutants.
(H) Rca1/emi1 coding region showing individual protein domains and the locations of point mutations (asterisks) found in hrpti245 and hrpx1 mutants.
Scale bar = 50 µm (D, E), 5 µm (F’, G’).