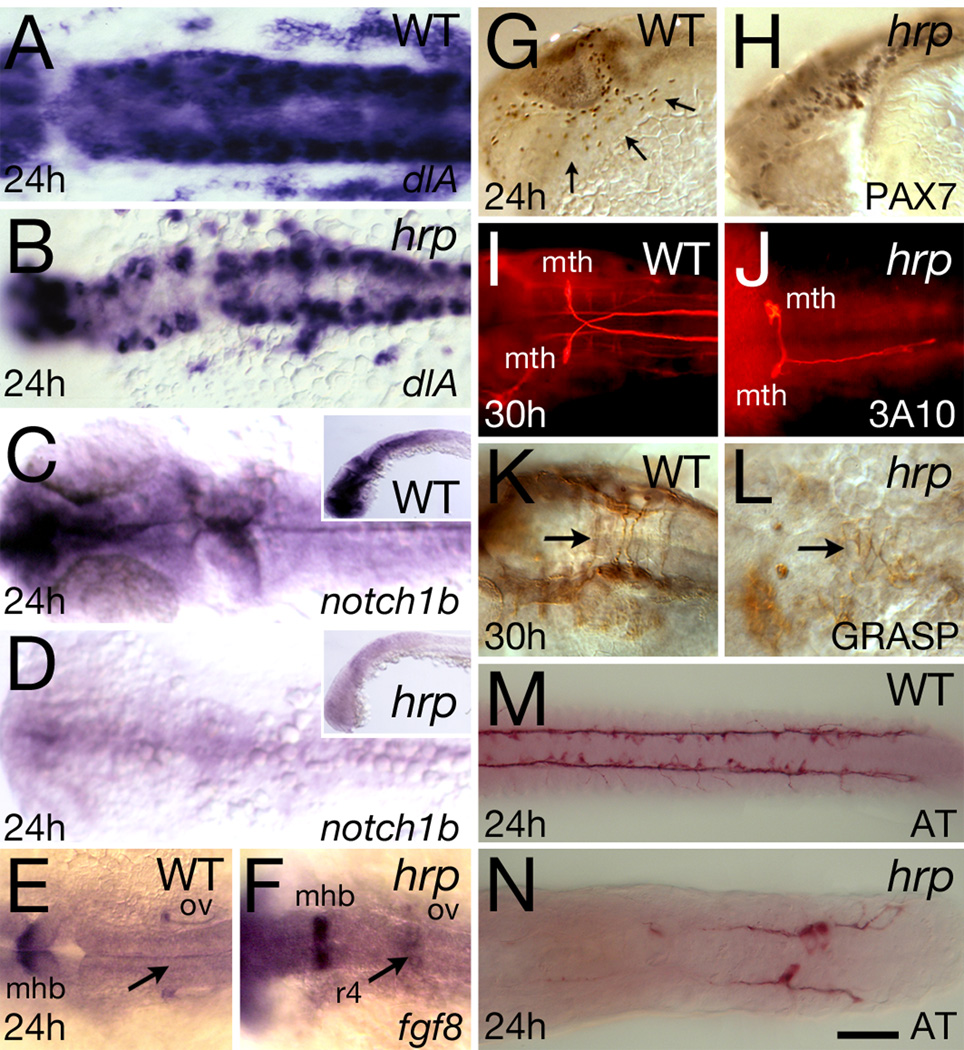
Fig. 5. Neural patterning defects in harpy mutants. Panels show wild-type control embryos and harpy mutants.
(A, B) Expression of deltaA (dlA) at 24 hours. Dorsal view of hindbrain. Note the normal intensity of expression in mutant cells.
(C, D) Expression of notch1b at 24 hours. Dorsal view of head; insets show lateral view. Note expression in mutants is almost absent.
(E, F) Expression of fgf8 at 24 hours. Dorsal view of hindbrain. Note ectopic staining in the 4th rhombomere of the mutant.
(G, H) anti-Pax7 staining at 24 hours. Arrows indicate neural crest cells migrating over the eye and pharyngeal arches; while these cells are present in the mutant, they are not seen on the migration pathway.
(I, J) dorsal view of 3A10-stained Mauthner neurons at 30 hours, displaying abnormal pathfinding and absence of axons in the mutants
(K, L) anti-Grasp staining at 30 hours; dorsal view of the hindbrain. Arrows indicate commissural neurons that in the mutant are chaotic.
(M, N) anti-acetylated tubulin (AT) staining at 24 hours; dorsal view of the trunk. Although axons are present in mutants, they do not express acetylated tubulin except in the tail region.
Abbr:
mhb, midbrain hindbrain border;
mth, Mauthner neurons.
ov, otic vesicle;
r4, 4th rhombomere;
Scale bar = 50 µm (A–D), 20 µm (F, G), 100 µm (E–N).