Fig. 8. harpy acts both cell autonomously and non-autonomously.
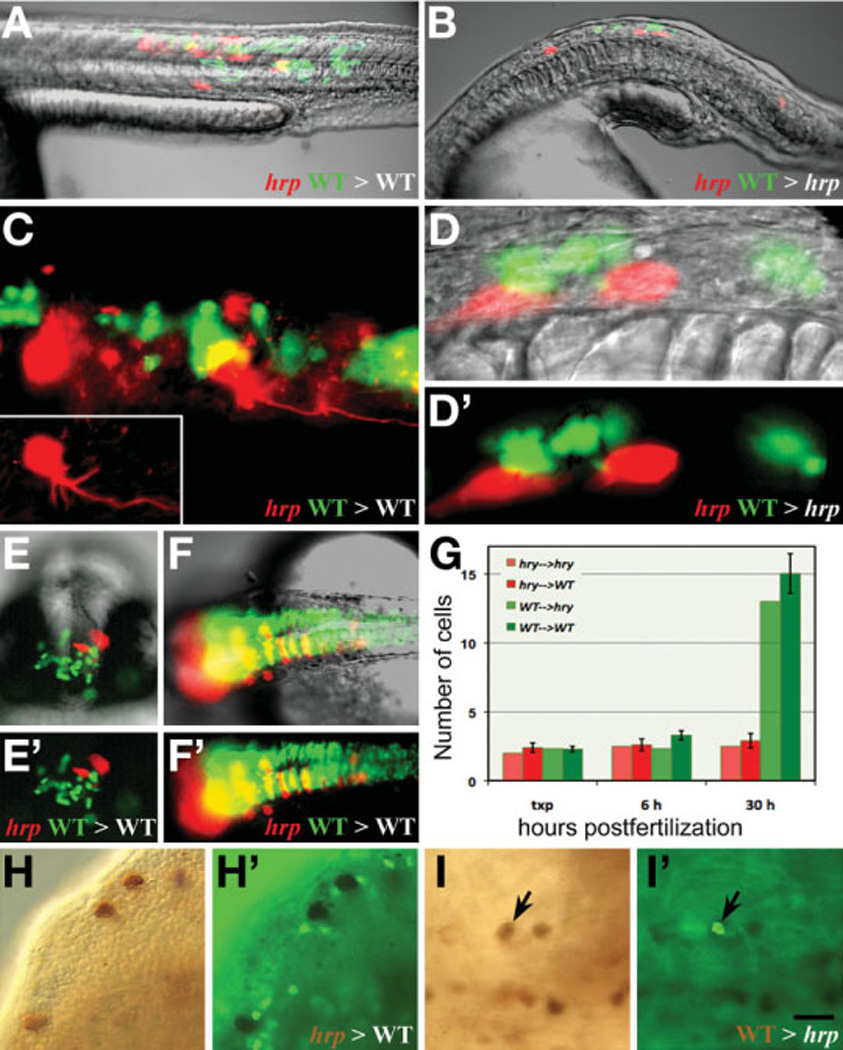
- (A,B) Composite images of a neural and muscle chimera.
- (C) UV image showing a magnified view of neural and muscle chimera in A. Inset shows single harpy interneuron which projected an axon.
- (D) magnified views of neural chimera in B. Note that the wild-type cells did not project axons.
- (E) Facial view of telencephalic region and
- (F) dorsal view of brain neural clones. Note that wild-type cells frequently cross the midline; mutant cells tend to not.
(G) Comparison of number of cells in clones. For each chimera, 2 to 3 cells from two separate individuals were placed into a host embryo at 5 hours, and recorded immediately afterwards (txp), then at 6 hours and again at 30 hours.
- (H, H’) Labeled mutant cells transferred to an wild-type host; mutant cells are not dividing.
- (I,I’) Labeled wild-type cells transferred to an unlabeled mutant host. A dividing wild-type cell is indicated (arrow).
Scale bar =200 µm (A,B,E,F), 50 µm (C,D), 100 µm (F,I).
