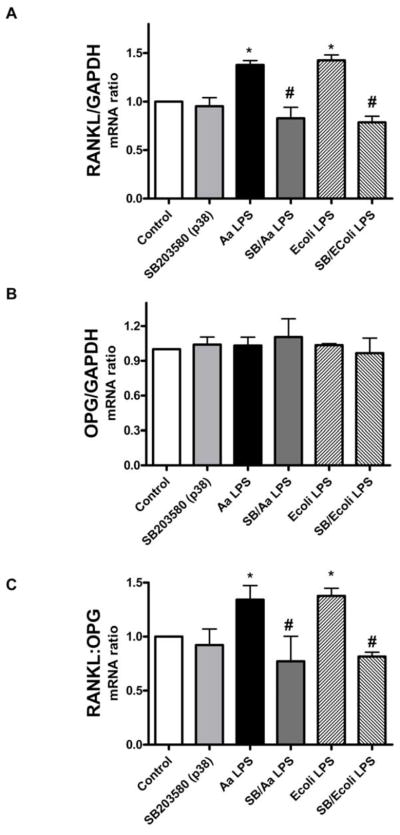
Figure 2. p38 MAPK regulates preferentially RANKL in LPS-stimulated PDL cells.
mPDL cells were grown to near confluency and de-induced in media containing 0.3% FBS for 8 h. The specific inhibitor for p38 MAPK (SB203580) was added to the culture medium at 10 μM 30 minutes before the 18 h stimulation with 1 μg/mL of LPS from E.coli and A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS. Total RNA was harvested and RT-PCR was performed and quantitated using GelDoc System. Results indicate that inhibition of p38 MAPK reduced LPS-induced RANKL mRNA expression, especially after E.coli LPS stimulation (A). No significant regulation of OPG mRNA expression was observed following p38 inhibition (B). The decrease on RANKL expression was sufficient to reduce the RANKL:OPG ratio (C). Figures are representative of three independent experiments and bar graphs indicate mean ± standard deviation of normalized fold changes of normalized gene expression. *Indicates significant difference (p<0.05) on mRNA expression in comparison to unstimulated cells. # indicates significant difference (p<0.05) on mRNA expression in comparison to LPS treated cells.