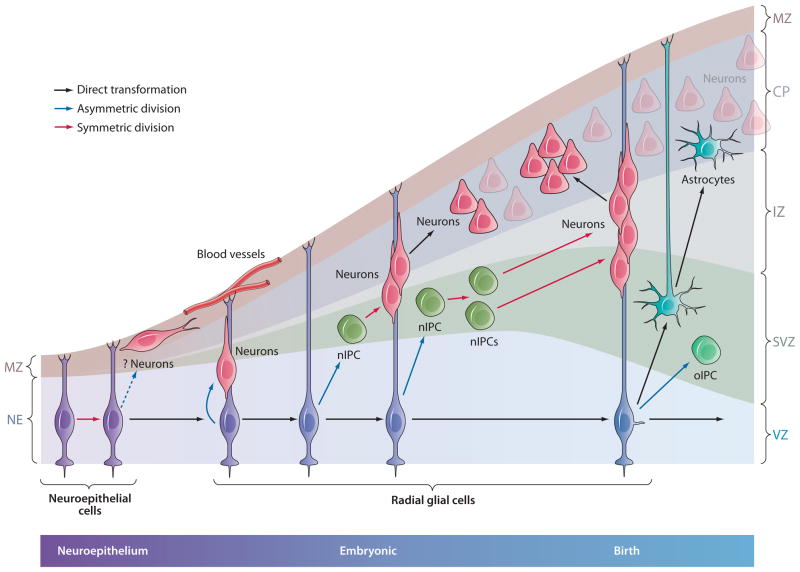
Figure 3.
Three modes of neurogenesis during cortical development. RG in cortex generate neurons (a) directly through asymmetric division; (b) indirectly by generation of nIPCs and one round of amplification; or (c) indirectly again through nIPCs, but with two rounds of division and further amplification. This additional amplification stage may be fundamental to increase cortical size during evolution (see text). Subpopulations of nIPCs are likely to divide more than once in subcortical brain regions, but this has not yet been documented. For additional details, see Figure 1. CP, cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; MZ, marginal zone; nIPC, neurogenic intermediate progenitor cell; RG, radial glia; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone.