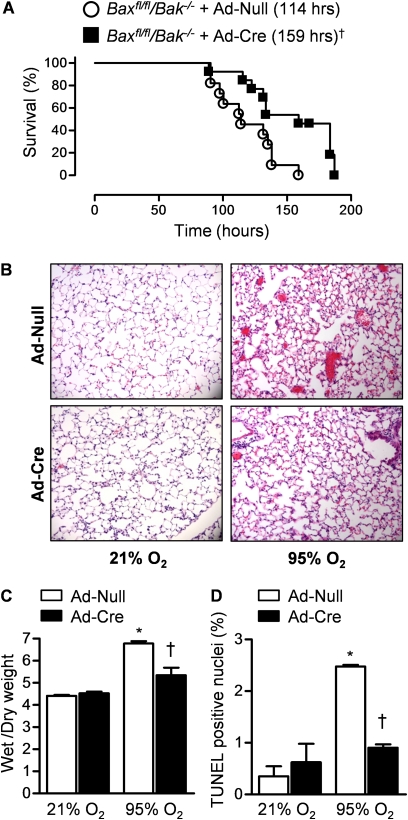
Figure 5.
BAX or BAK contribute to hyperoxia-induced mortality in mice. (A) Baxfl/flBak−/− mice were intratracheally infected with an adenovirus encoding no transgene (Ad-Null) or one encoding Cre recombinase (Ad-Cre) (1 × 109 pfu/animal) 30 days before exposure to hyperoxia (≥ 95% O2) for measurement of survival (n = 11 for Ad-Null; n = 13 for Ad-Cre; †indicates P < 0.001 for comparison between Ad-Null and Ad-Cre infected mice after exposure to hyperoxia). Identically treated Baxfl/flBak−/− mice were exposed to hyperoxia or room air for 84 hours for assessment of lung injury. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin stained lung sections (original magnification ×100). (C) Wet-to-dry weight ratios of the lung. (D) Percentage of TUNEL-positive nuclei. n ≥ 4 for all measures. *P < 0.05 for comparison with normoxic controls. †P < 0.05 for comparison of difference between Ad-Null and Ad-Cre transfected animals after exposure to hyperoxia.