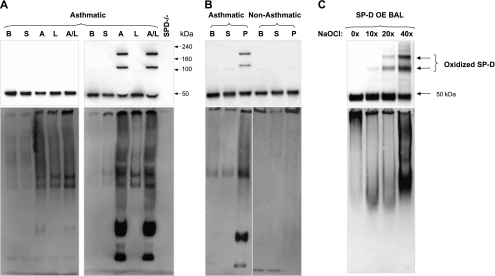
Figure 1.
Challenge with allergen causes cross-linking of human surfactant protein D (SP-D) and alters its quaternary structure. (A) Blots from two subjects of the entire study group (n = 15) who underwent segmental challenges are shown. The left blots are from a representative subject who did not develop cross-linked SP-D (n = 8) and the right blots are from a representative subject who developed cross-linked SP-D (n = 7). Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from patients with asthma at baseline (B), and after challenge with either saline (S), house dust mite allergen (A), LPS (L), or a combination of allergen with LPS (A/L) was analyzed for total SP-D level by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) under reduced conditions (top) or by native gel electrophoresis to determine quaternary structure of SP-D (bottom). BAL from SP-D–deficient mice (SP-D−/−) was run as a negative control for nonspecific bands. Quantity of cross-linked SP-D as a percentage of total SP-D per group (A and A/L) is given in the result section and individual data are provided in Figure 4. (B) Blots from two representative subjects from a different challenge study are shown. BAL fluid from one subject with asthma (left lanes) and one healthy subject (right lanes) at baseline (B), and after challenge with saline (S) or mixed grass pollen allergen (P) were analyzed as in A. (C) Oxidative cross-linking of SP-D in vitro. BAL from mice overexpressing rat SP-D (OE BAL) was treated with various doses of NaOCl and reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions (top) or by native gel (bottom) followed by immunoblotting with anti–SP-D antibody. Shown data are representative of five independent experiments.