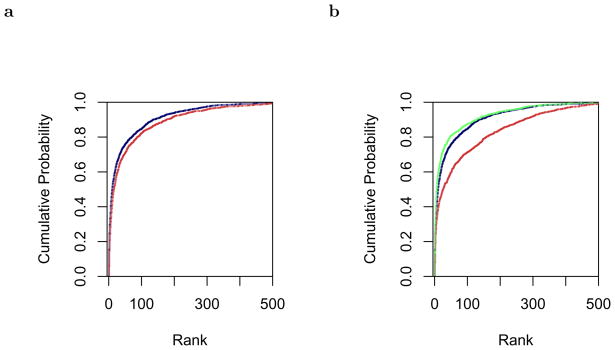
Figure 5.
Performance on free association norms. Similarity ratings were evaluated for a list of 1040 words paired with their strongest associates. The strength of the relationship between the prime and its first associate was calculated and turned into a rank relative to the first associates of the other primes. Cumulative probability distributions of ranks are shown. Lower ranks reflect better model performance, meaning that higher curves reflect better model performance. a. The cumulative probability distribution of ranks of the first associates for the pTCM “recall” model (dark blue) and the pTCM vector space model (light red). For the pTCM recall model, the semantic representation of the cue item was used as a cue via the context-to-item matrix. The activation of each target was used to generate its rank. The vector space model simply uses the inner product of the semantic representation of items to generate similarity values. b. Cumulative probability distributions of ranks for the pTCM recall model (dark blue), LSA trained on the same words (light red) and LSA trained on the entire corpus (lighter green). pTCM trained on the reduced corpus shows dramatic improvement over LSA when it was trained on the same words. LSA trained on the entire corpus shows a modest improvement over pTCM trained on the reduced corpus.