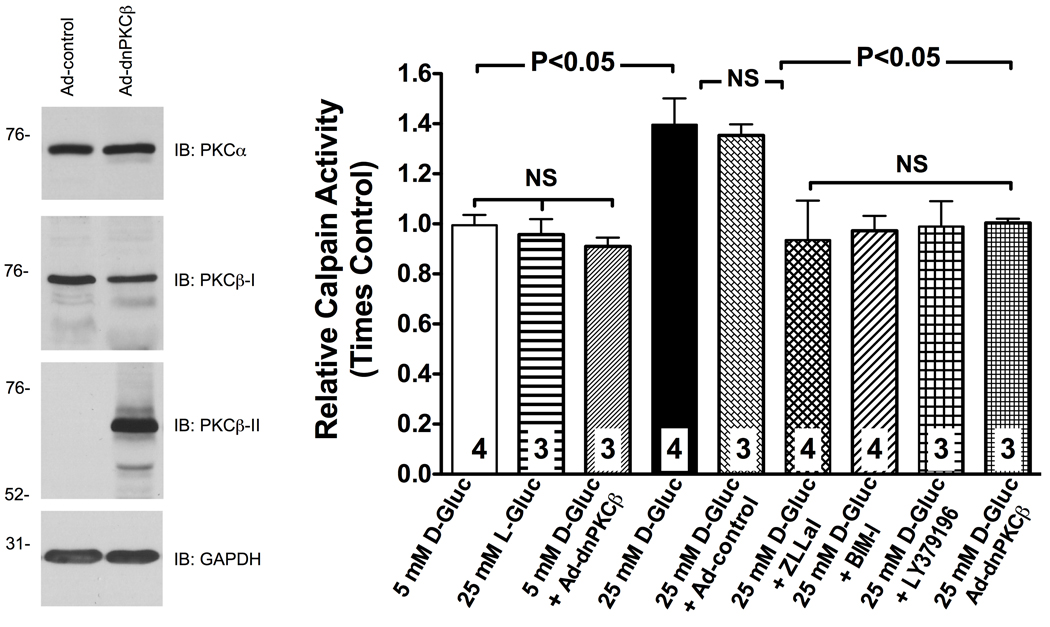
Figure 3. RHMEC experience a PKCβ-dependent increase in calpain activity in response to high glucose.
Calpain activity was measured in attached RHMEC using the fluorogenic substrate Succ-LLVY-AMC and expressed as fold change from control. Genetic inhibition of PKCβ by expression of a kinase-inactive dominant-negative (dn) PKCβ, and pharmacological inhibition of either total PKC activity with BIM-I or selective PKCβ activity with LY379196 prevented upregulation of calpain in response to high glucose. The mutant protein constructed on rabbit PKCβ-II cDNA could be distinguished from the endogenously expressed PKCβ-I by antibodies raised against c-terminus of PKCβ-I and PKCβ-II. Expression of PKCα was not affected by the dnPKCβ over-expression (Immunoblot). The dnPPKCβ used in this study has been shown to inhibit select functions mediated by both PKCβ-I and PKCβ-II, but not by other PKCs such as PKCα44. Bars represent mean ± SEM, and numbers at the base of the bars represent the number of experiments.