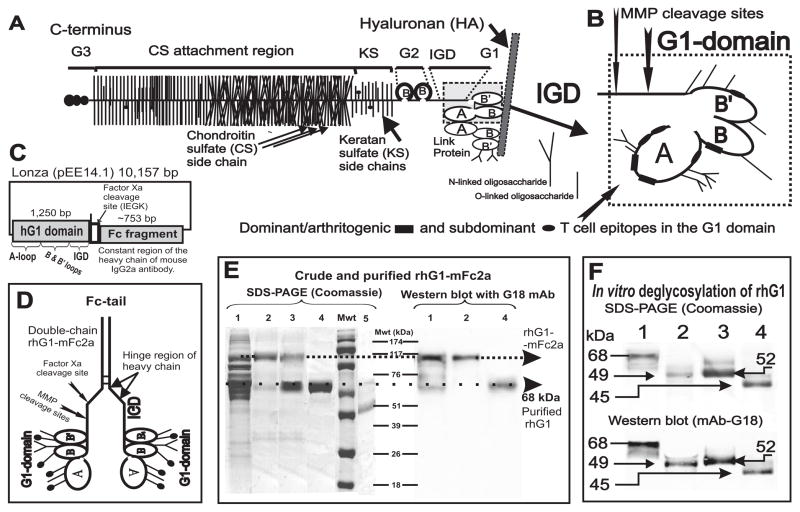
Figure 1.
Schematics of the cartilage proteoglycan (PG) aggrecan, G1 domain, the mammalian expression vector containing the rhG1 fusion construct, and the analysis of expressed recombinant proteins. A, The PG molecule consists of a protein core to which hundreds of glycosaminoglycan side chains (chondroitin sulfate [CS] or keratan sulfate [KS] are attached together with O-linked and N-linked oligosaccharides. The B and B’ loops of the G1 domain of the aggrecan PG core protein (PG monomer) interact with hyaluronan (HA) in cartilage; this interaction is stabilized by link protein (LP). Core protein structure: G1, G2 and G3 are the globular domains; IGD is the interglobular domain; KS is the keratan sulfate-rich domain; CS is the chondroitin sulfate attachment region (this figure is an adaptation of figures from references (19) and (5)). B, Detailed structure of the G1 domain, including the major cleavage sites for stromelysin (MMP3) and two aggrecanases (ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5). Three dominant/arthritogenic and four subdominant epitopes are located in the G1 domain (20,21). Thus, less than 0.02% of the molecular mass, or less than 15% of the core protein (i.e., the G1 domain), drives the arthritogenic response to PG in genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. C, The rhG1-Xa-mFc2a construct in a Lonza pEE14.1 mammalian expression vector. D, Schematics of the “double-chain” rhG1-mFc2a fusion protein. The C-terminal end of the heavy chain of mouse IgG2a (Fc tail) is linked, via the hinge region, to the G1 domain of PG. The heavy chains are able to reform the disulfide bridges. A properly folded Fc tail binds to Protein A or Protein G, thus allowing for purification by affinity chromatography. E, Detection of the rhG1-Xa-mFc2a protein, separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue G-250 (left-hand panel) and separated by western blot and stained with mAb G18 (right–hand panel). Lane 1: unpurified CHO serum-free medium harvested from rhG1-Xa-mFc2a-transfected and cloned CHO cells (roughly 30 μg protein). Lane 2: Protein G-purified rhG1-Xa-mFc fusion protein from the same CHO-SFM (5 μg protein). Lane 3: purified rhG1-Xa-mFc2a fusion protein after cleavage with factor Xa. Lane 4: rhG1 protein re-purified using Protein G/Sepharose. Lane 5 contains highly purified native human G1 domain (~42 kDa) isolated from human cartilage PG as previously described (19). Molecular weight markers (Mwt) are indicated in kDa. F, In vitro de-glycosylation of rhG1 yields a lower molecular mass protein. Lane 1: purified rhG1 without Fc-tail. Lane 2: rhG1 digested with PNGase F (thus removing all N-linked oligosaccharides). Lane 3: rhG1 digested with keratanases 1 and 2. Lane 4: digested with all enzymes (PNGase F, keratanases, sialidase and O-glycosidase), thus removing both N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharides.