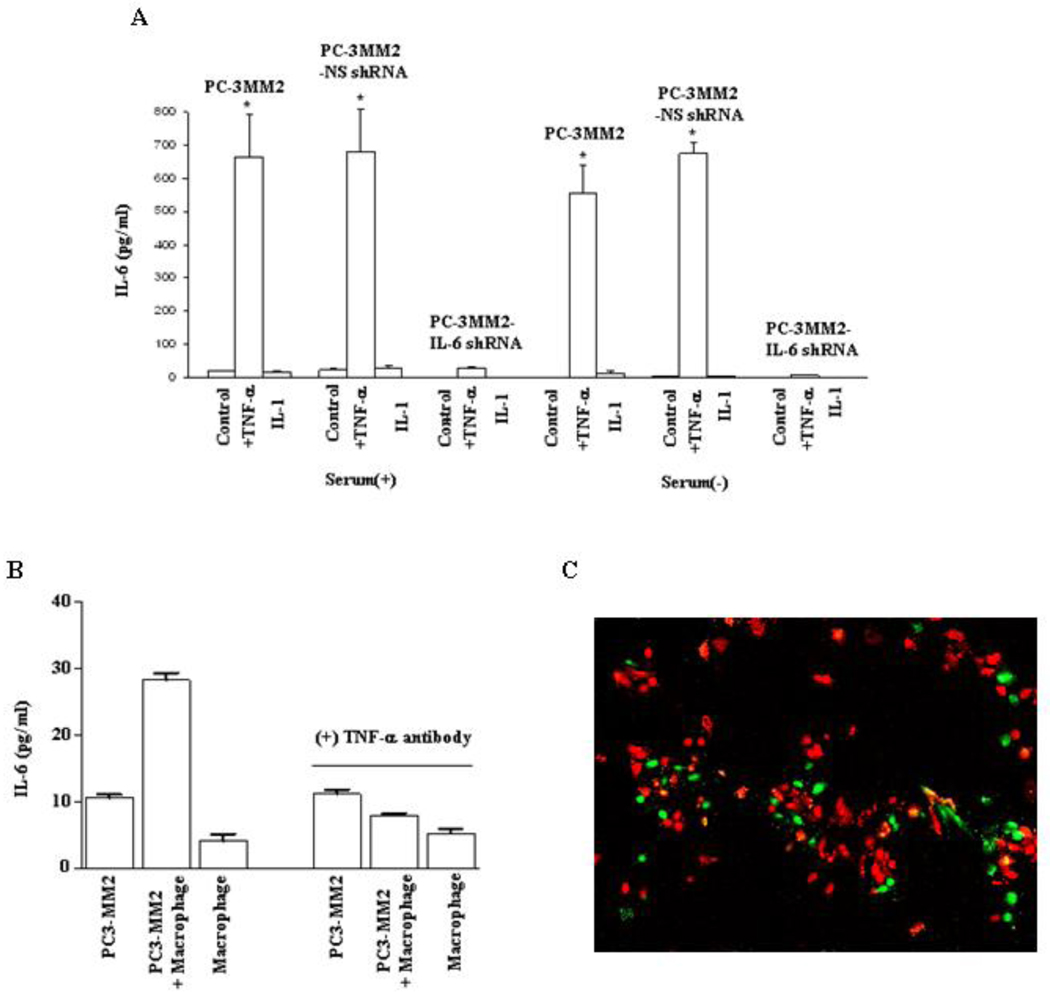
Fig. 1.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. A: PC-3MM2, PC-3MM2-NS shRNA, and PC-3MM2-IL-6 shRNA human prostate cancer cells (1 × 105) were plated into 96-well plates and cultured in MEM with or without 10% fetal bovine serum. Cells were treated with PBS (control), TNF-α (10 ng/ml), or IL-1 (100 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Supernatants were collected and measured for the level of IL-6 by ELISA. Transfection of PC-3MM2 cells with IL-6 shRNA significantly decreased the production of IL-6 and exogenous TNF-α did not lead to increased production of IL-6. Stimulation with IL-1 did not affect the production of IL-6. B: PC-3MM2 cells (1 × 105), immorto-mouse peritoneal macrophages (1 × 105), or PC-3MM2 cells and immorto-mouse peritoneal macrophages (cell ratio, 1:1; total 1 × 105) were plated into 96-well plates and cultured in MEM with 20% FBS. Cells were treated with PBS or anti-TNF-α antibody (0.5 µg/ml) for 24 hours. Co-cultures of PC-3MM2 with immorto-mouse peritoneal macrophages significantly increased the production of IL-6, and the stimulatory effect of macrophages on the production of IL-6 was neutralized by anti-TNF-α antibody (0.5 µg/ml). C: Co-localization of IL-6 and F4/80 by immunofluorescence analysis. Tumor cells (F4/80-negative) were positive for IL-6 staining (green). Macrophages (F4/80-positive; red) were IL-6-negative.