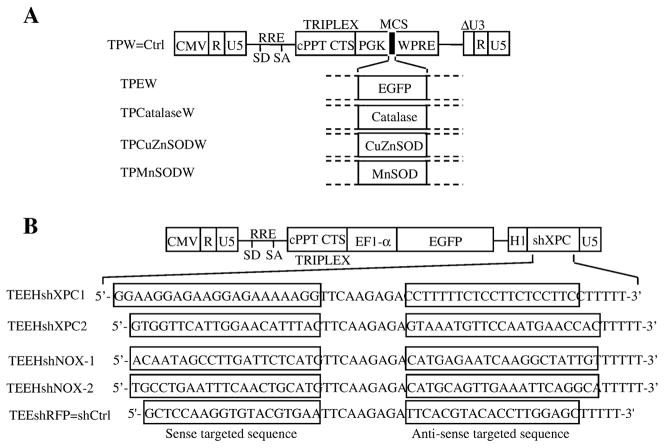
Figure 1. Vector constructs and analysis of the transduction efficiency.
(A) Lentiviral vectors constructs used to overexpress EGFP, catalase, CuZnSOD, or MnSOD are shown. Vectors carry an internal cassette for the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), catalase, CuZnSOD, or MnSOD driven by the promoter of human phosphoglycerate kinase gene (hPGK).
Δ U3, R, and U5 are the LTR regions, with a deletion that includes the enhancer and the promoter from U3. CMV is the cytomegalovirus promoter, SD is the major splice donor site, SA is the splice acceptor site, RRE is the rev-response element, cPPT is a nuclear import sequence, and WPRE is a regulatory element of woodchuck hepatitis virus. (B) Lentiviral constructs used to inhibit XPC, NOX1, NOX2, or red fluorescent protein (RFP) expressions are shown. TEEHshRFP construct was used as the control shRNA (named shCtrl) plasmid.